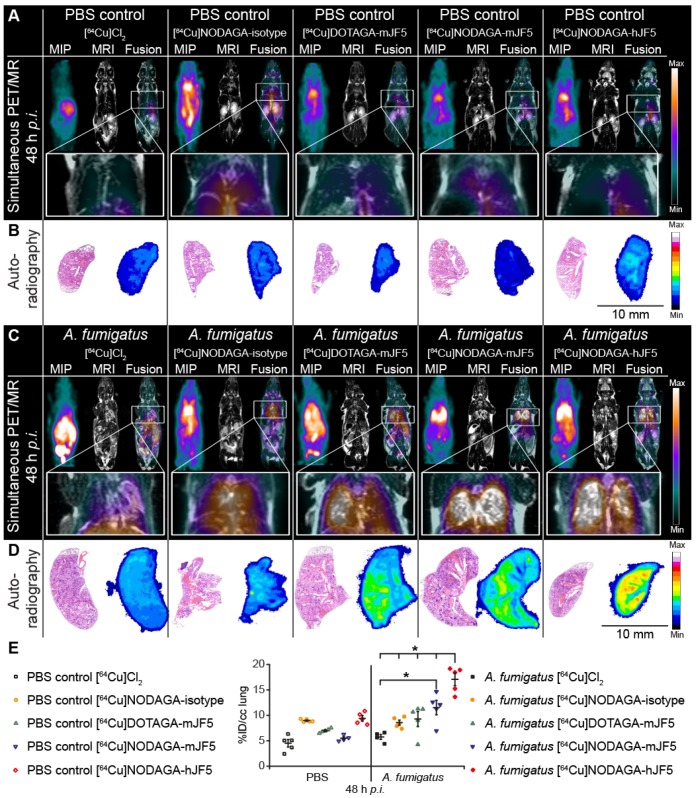
Figure 4.
In vivo biodistribution of [64Cu]Cl2, [64Cu]NODAGA-isotype control antibody ET901, [64Cu]DOTAGA-mJF5, [64Cu]NODAGA-mJF5 and [64Cu]NODAGA-hJF5 in PET/MR imaging at 48 h p.i. A and C. Coronal MIP, MR and fused PET/MR images of PBS treated mice and A. fumigatus infected mice injected with the respective tracers. The MR images of infected animals clearly reveal pulmonary infection and hyphal growth of A. fumigatus (hyperintense regions). The PET insert images of infected mice display specific lung uptake of the radiolabeled JF5 antibody-tracers compared to infected animals receiving [64Cu]Cl2 only or the 64Cu-labeled isotype control antibody ET901. Additionally, the high liver uptake of [64Cu]Cl2 and [64Cu]DOTAGA-mJF5 in infected animals can be observed. B and D. Representative autoradiographic images with subsequent H&E staining of the lung tissue 48 h p.i. Autoradiographs of lung sections (right) with the corresponding H&E staining (left). Ex vivo autoradiography shows higher tracer accumulation in the lungs of infected animals receiving the JF5 antibody tracers compared to the respective PBS controls. Infected animals receiving the JF5 antibody tracers show higher signal intensities in the lung compared to the A. fumigatus infected mice receiving [64Cu]Cl2 or the control tracer [64Cu]NODAGA-isotype. Furthermore, higher uptake of [64Cu]NODAGA-hJF5 in the lungs of infected animals compared to the other infected groups can be observed. (E) Quantification of the PET images 48 h p.i. for lung tissues. Uptake of the various tracers in the lungs of infected animals compared to PBS controls at 48 h p.i. is shown in groups of n=4-5 mice. Significantly higher uptake of [64Cu]NODAGA-hJF5 in the lungs of A. fumigatus infected animals was obtained compared to all other tracers. Significantly higher lung uptake was also observed in infected animals injected with the tracer [64Cu]NODAGA-mJF5 compared to [64Cu]Cl2 . Data are expressed as the mean ± SD %ID/cc. Group differences were examined using one-way ANOVA, followed by post hoc Tukey-Kramer, *P < 0.05.