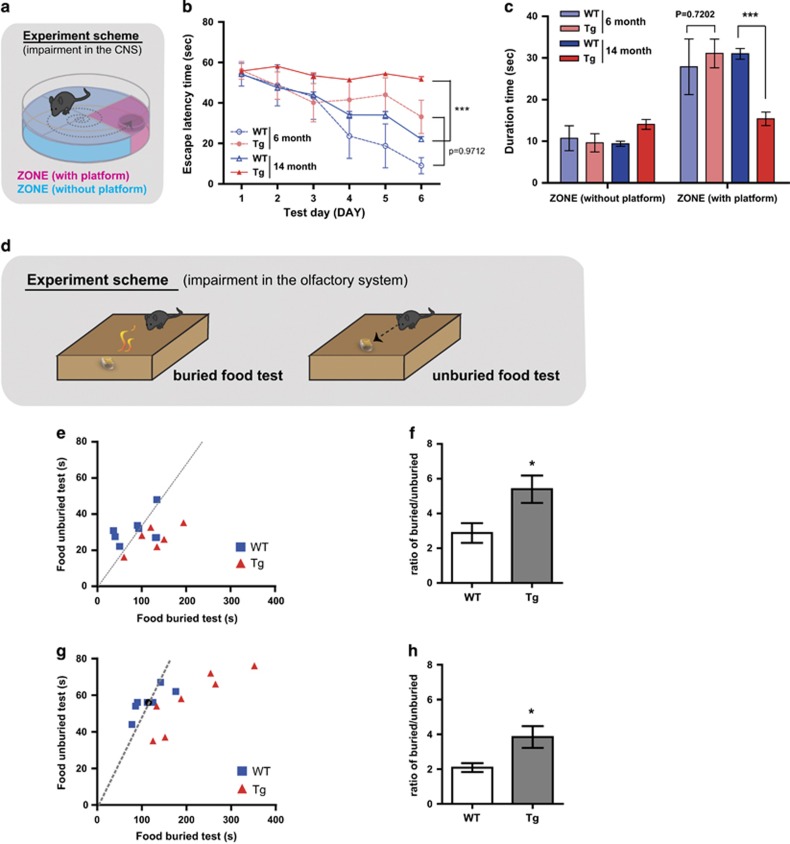
Figure 1.
Olfactory impairment appears in 6-month-old Tg2576 mice without failure of spatial learning and memory. (a) The Morris water maze task was performed at 6 months (WT, n= 4; transgenic Tg2576 (Tg), n= 6) or 14 months of age (WT, n = 17; Tg, n= 16). (b) Training trials were conducted and the escape latency was measured for 6 days. ***P<0.001 by two-way ANOVA, using Prism software (GraphPad software). (c) The probe test was conducted 48 h after the final training session. A platform was located in zone with platform, and the durations that the mice of each group stayed in the zone without platform and the zone with platform were measured. ***P<0.001 by two way ANOVA, using Prism software (GraphPad software). (d) Illustration of scheme for buried/unburied food test. (e and f) Buried and unburied food tests in 6-month-old mice (WT, n=8; Tg, n=8). The latencies (e) to find buried or unburied food and their ratios (f) were measured (slope in the latencies graph (e) represents the average time to find buried or unburied food in WT mice) (g and h) Buried and unburied food tests in 14-month-old mice (WT, n=8; Tg, n=8). The latencies (g) to find buried or unburied food and their ratios (h) were measured (slope in the latencies graph (g) represents the average time to find buried or unburied food in WT mice) All data are presented as mean±S.E.M. Two-way ANOVA, using Prism software (GraphPad software), *P<0.05 and ***P<0.001 denote statistical significance