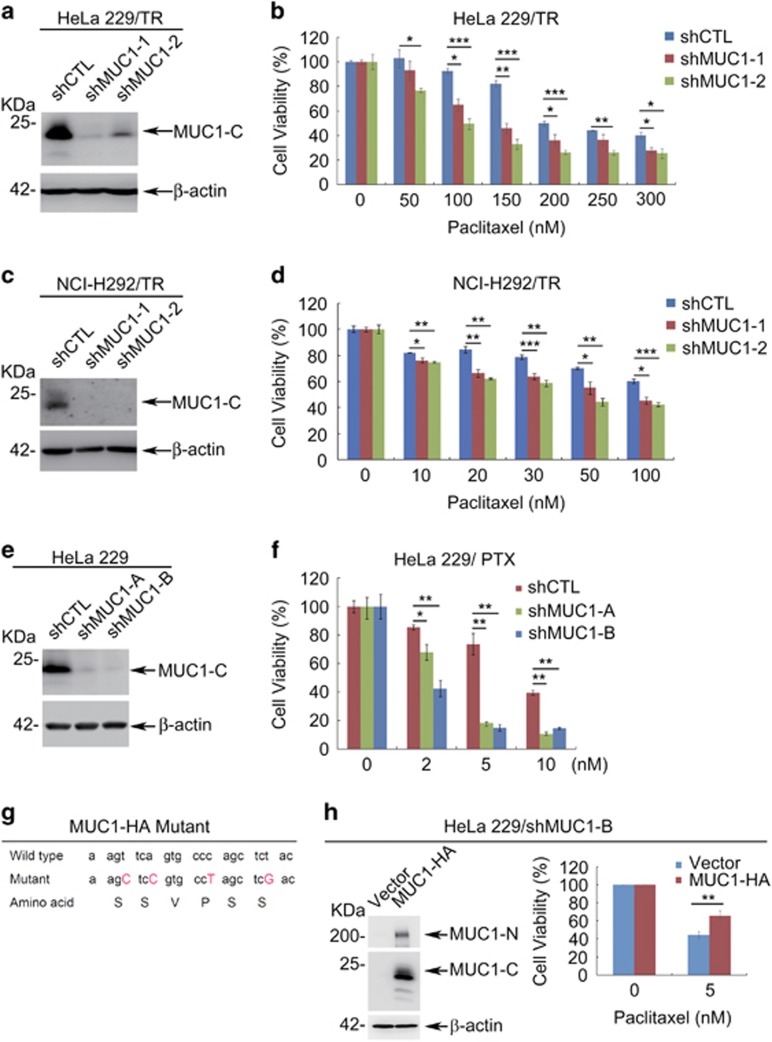
Figure 2.
MUC1 modulates chemosensitivity in cancer cells. (a) Western blot of indicated proteins in HeLa229/TR/shCTL and HeLa229/TR/shMUC1 cells with β-actin as a loading control. (b) HeLa229/TR/shCTL and HeLa229/TR/shMUC1s cells were seeded in 96-well plate (6000 cells per well), cultured overnight and then treated with different concentrations of PTX for 48 h. Cell viability was measured by CCK8 assay. (c) Western blot of indicated proteins in NCI-H292/TR/shCTL and NCI-H292/TR/shMUC1 cells with β-actin as a loading control. (d) NCI-H292/TR/shCTL and NCI-H292/TR/shMUC1 cells were seeded in 96-well plate (10000 cells per well), cultured overnight and then treated with different concentrations of PTX for 48 h. Cell viability was measured by CCK8 assay. (e) HeLa229 cells were stably transfected with pRNAU6.1-shCTL, pRNAU6.1-shMUC1-A or pRNAU6.1-shMUC1-B plasmids and subjected to western blot with indicated antibodies. (f) HeLa229/shCTL and HeLa229/shMUC1 cells were treated with different concentrations of PTX for 48 h. CCK8 assays were applied to detect cell viability. (g) A diagram of wild-type and synonymous mutated MUC1 sequences. (h) HeLa229/shMUC1-B cells were transfected with shMUC1-B-resistant pIRESpuro2-MUC1-HA (MUC1-HA) or vector plasmids. Western blot was carried out to identify the expression of MUC1 (left). Cells were treated with DMSO (0 nM) or 5 nM of PTX for 48 h. CCK8 assays were applied to detect cell viability (right). Data are shown of three independent experiments, mean±S.D. (n=3)