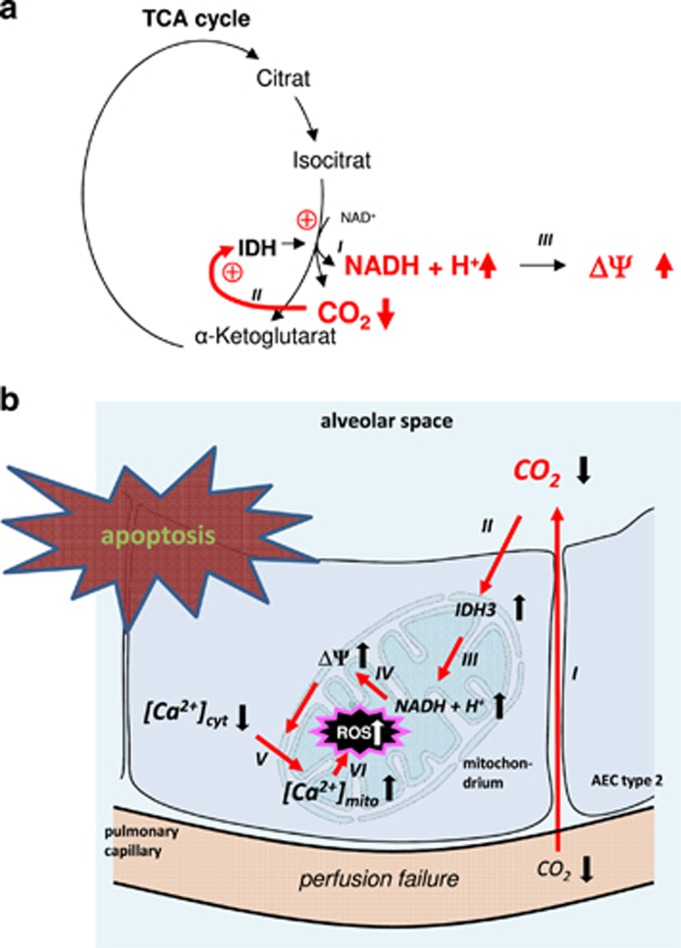
Figure 7.
(a) IDH3 catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate, producing α-ketoglutarate and CO2 while converting NAD+ to NADH (I). Because IDH3 activity is negatively regulated by its product CO2 we conclude that under hypocapnic conditions IDH3 activity (II) and thus NADH production (III) rises. (b) Proposed sequence of events underlying Ca2+-dependent CO2-sensing mechanism. Alveolar perfusion failure in ventilated lung regions, equivalent to a VD/VT increase, leads to alveolar hypocapnia (I). Alveolar hypocapnia elevates IDH3 activity via a feedback mechanism (II). In turn, NADH (III) production and ΔΨ (IV) increases leading to a calcium shift from cytosol into the mitochondrium (V). Further, the hypocapnia-induced mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake leads to mitochondrial ROS production (VI). Finally, the mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake and/or ROS production results in apoptosis