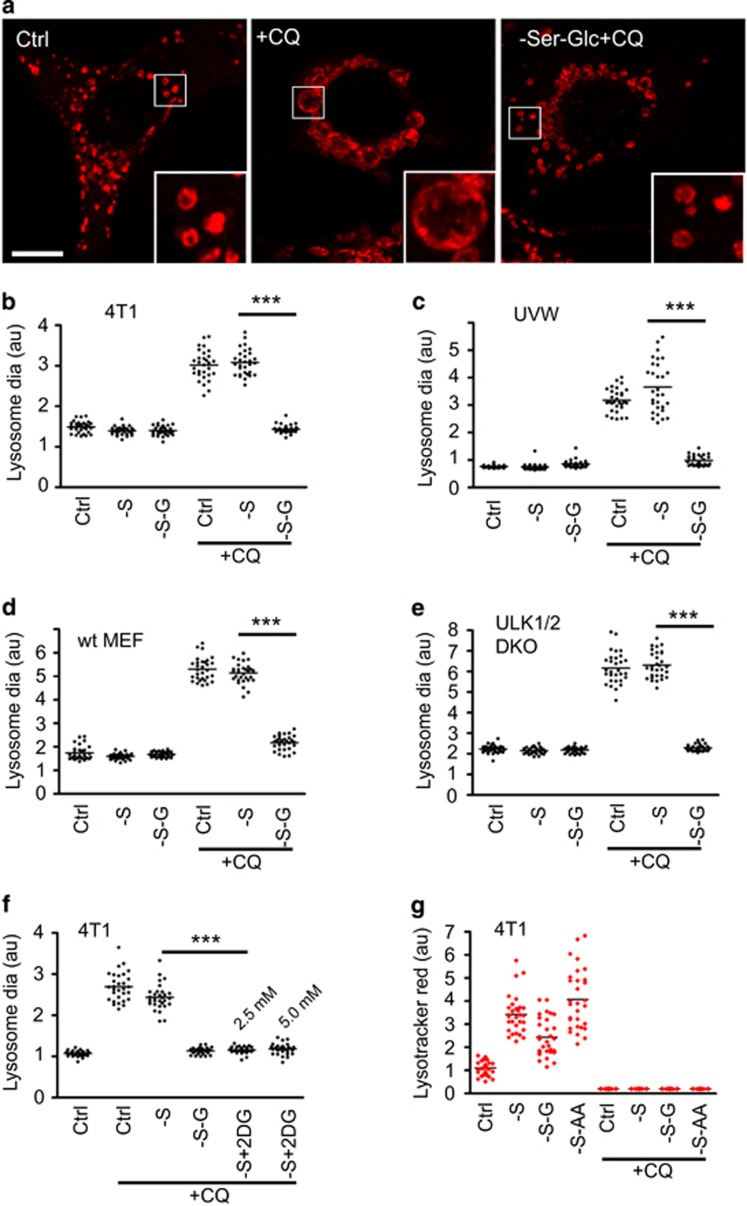
Figure 6.
CQ induces lysosomal swelling, which is blocked upon glucose starvation. (a) 4T1 cells were treated with full-nutrient media (Ctrl); serum starvation; or serum and glucose starvation±CQ (25 μM) as indicated for 8 h. Cells were fixed and stained for lysosomal-associated membrane protein-1 (LAMP-1). CQ induces robust lysosome swelling, but this is reversed upon glucose starvation, as highlighted in boxed insets. Scale bar: 10 μm. (b) Quantification of lysosomal size in 4T1 cells described in (a). Average lysosomal diameters were measured for 30 cells per condition (each cell as a datum point, shown as relative arbitrary units). Reversal of CQ-induced lysosomal swelling by glucose starvation was conserved in: (c) UVW glioma cells, (d) wild-type MEF and (e) ULK1/2 DKO MEF. (f) 4T1 cells were treated with serum (and glucose starvation) or alternatively with 2DG (2.5 or 5 mM) ±CQ (25 μM) as indicated for 8 h. Cells were quantified for lysosome swelling. (g) 4T1 cells were treated with full-nutrient media; serum starvation; or serum and glucose starvation ±CQ (25 μM) as indicated for 4 h. Lysotracker red DND-99 (50 nM) was added for the final 30 min of treatment. Cells were analysed by confocal microscopy for lysotracker intensity (30 cells per condition). CQ deacidified lysosomes under all nutrient conditions. All data shown are representative of at least three independent experiments. ***P<0.001 by one-way ANOVA