Fig. 1.
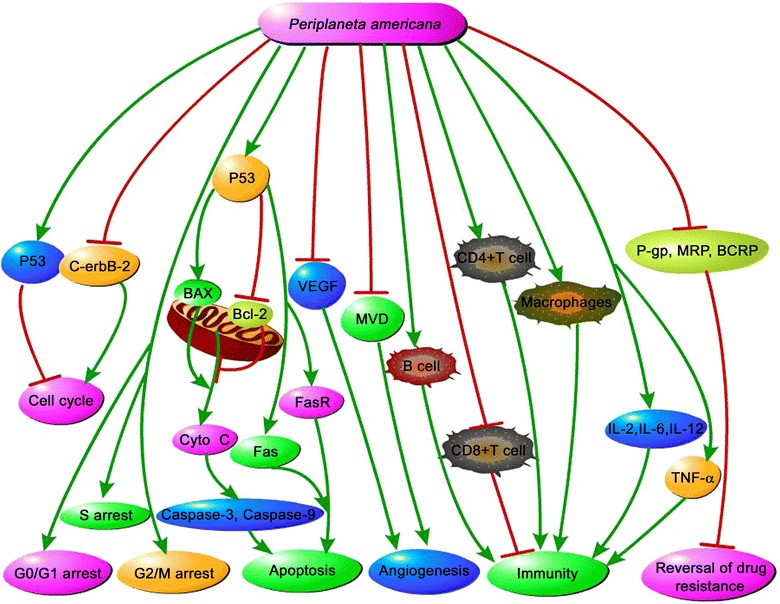
Diagraphic illustration of mechanisms of anti-tumor effects of P. americana. P. americana extract inhibited cell proliferation via p53- and C-erbB-2-mediated cell-cycle arrest in progesterone-receptor negative endometrial cancer cells. P. americana extracts induced cell-cycle arrest of Lewis lung carcinoma (3LL) cells and human lung cancer cells H125 at G0/G1 phase and S phase, respectively. “Kangfuxin Liquid” induced cell-cycle arrest of human gastric cancer cells BGC-823 at G2/M phase. P. americana extract decreased the ratio of Bcl-2 to BAX by increasing p53 and upregulated Fas and FasR expression, which induced apoptosis of cancer cells. P. americana may depress angiogenesis by inhibiting VEGF expression and microvessel density (MVD). P. americana extract activated lymphocytes, increased the CD4/CD8 ratio of peripheral blood, prompted T- and B-lymphocytes proliferation, and modulated cytokines release, including TNF-α, IL-2, IL-6, and IL-12. In addition, the extract effectively reversed the drug resistance of human hepatoma cells (HepG2/ADM) by targeting P-gp, MRP, and BCRP
