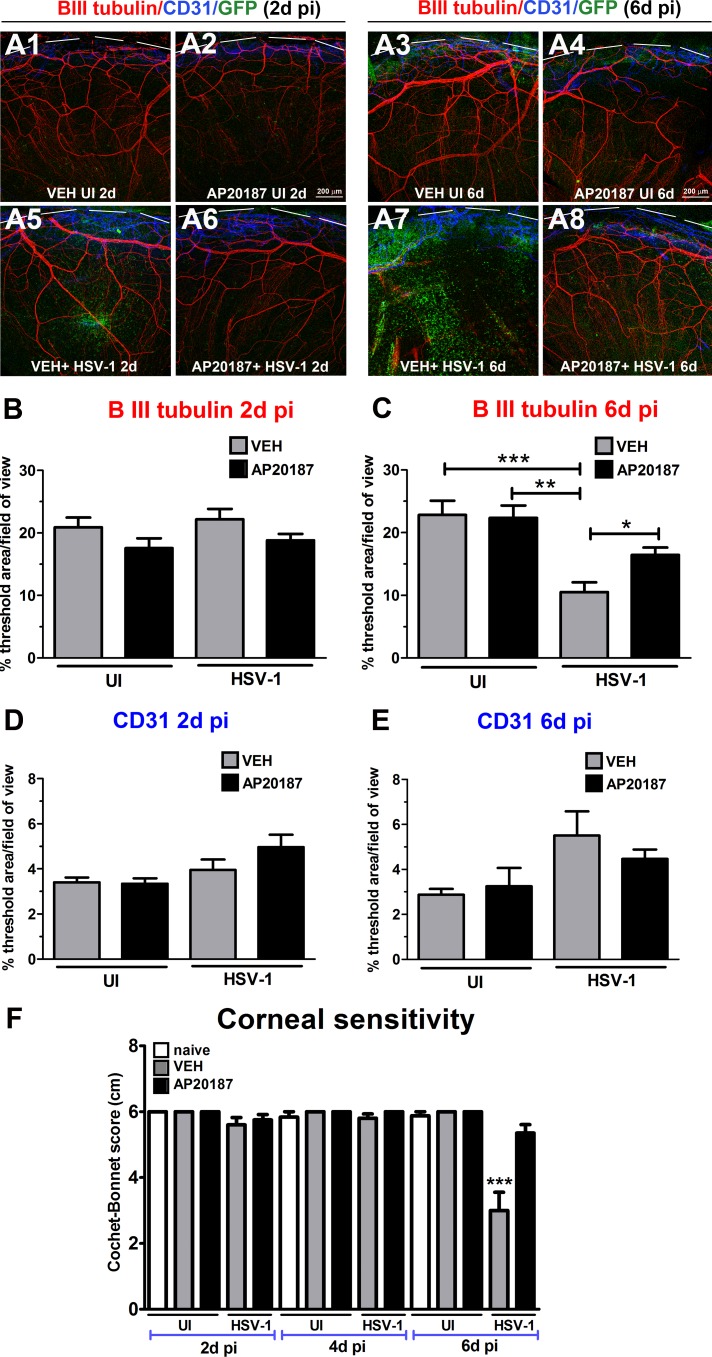
Figure 4.
Depletion of CSF-1R+ cells correlates with preservation of corneal nerve structure and function following HSV-1 infection. MAFIA mice were treated with daily IP injections of AP20187 dimerizer or VEH. Following the treatment, mice were infected with 103 PFU HSV-1/cornea or left UI as controls and their corneas harvested at 2 or 6 days PI for IHC assessment of corneal innervation and vasculature. (A1–A8) Representative confocal microscopy images of flat mount cornea preparations from UI and infected mice (at 2 and 6 days PI) previously treated with VEH or AP20187. Green: GFP+ cells (macrophages/monocytes/DCs); red: nerves (β III tubulin); blue: vessels (CD31); top discontinued white lines depict the limbus margins. Analysis of corneal innervation (B, C) and vascularization (D, E) at the indicated time points PI expressed as mean % threshold area positive for β III tubulin signal per field of view ± SEM and mean % threshold area positive for CD31 signal per field of view ± SEM, respectively. (B–D) n = 6 to 8 per infected group and n = 3 to 4 per UI group from two independent experiments; (C) n = 14 to 16 per infected group and n = 4 to 6 per UI group from three independent experiments; (E) n = 5 to 12 per infected group and n = 4 to 5 per UI group from two independent experiments. (F) Corneal sensitivity was assessed at 2, 4, and 6 days PI, prior to tissue collection. Bars depict mean Cochet-Bonnet score ± SEM for each group (n = 8–10 per infected group and n = 4–6 per UI group at 2 and 4 days PI from two independent experiments; n = 17–18 per infected group and n = 8–10 per UI group at 6 days PI from three independent experiments). (B–F) ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, and *P < 0.05 by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni multiple comparison test.