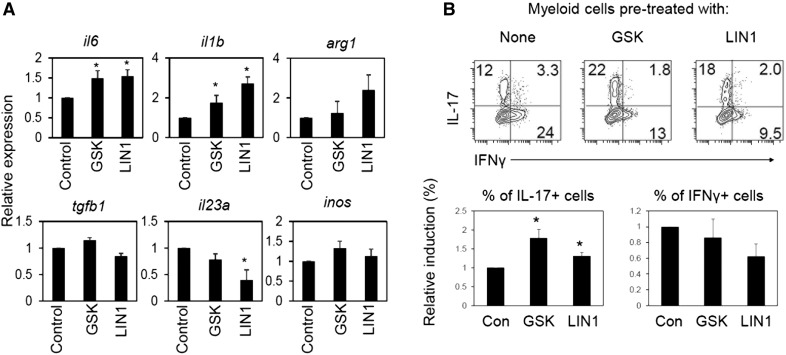
Figure 6. Inhibition of LRRK2 kinase activity affects myeloid cell differentiation and phenotype.
(A) Effects of LRRK2 kinase inhibitors on selected gene expression in bone marrow–derived myeloid cells. (B) Function of bone marrow–derived myeloid cells, pretreated with LRRK2 kinase inhibitors, in regulating CD4+ T cell differentiation into Th17 and Th1 cells. Rat bone marrow cells were differentiated with M-CSF (20 ng/ml) for 7 d in the presence of indicated LRRK2 inhibitors (GSK2578215A or LRRK2-IN-1) and then activated with LPS for 24 h before quantitative RT-PCR analysis of indicated genes in (A) or for coculture in (B). LPS-activated myeloid cells were cocultured with rat spleen CD4+ T cells in the presence of SEB (5 μg/ml) for 5–6 d, and frequencies of IL-17+ Th17 cells and IFN-γ+ Th1 cells were examined after coculture. Representative dot plots and pooled data (n = 5) are shown. *Significant differences (P ≤ 0.05) from control groups. Error bars indicate means ± sem.