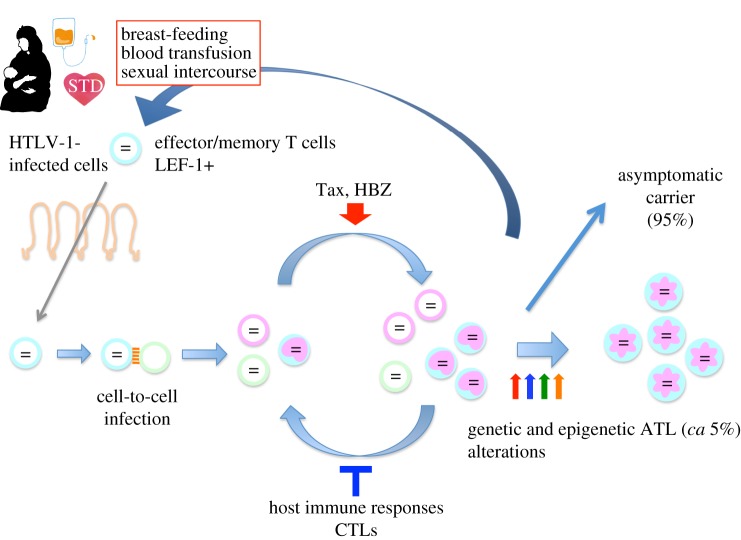
Figure 2.
Natural history of HTLV-1 infection. HTLV-1 transmits via three different routes: (i) breast-feeding, (ii) sexual intercourse, and (iii) the parenteral route. After infection, the virus increases the number of infected cells in vivo through the actions of Tax and HBZ. The host immune response suppresses HTLV-1-infected cells, mainly through lysis by virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). HTLV-1-infected cells possess the immunophenotype of effector/memory T cells, which migrate into breast milk and semen; these infected cells can transfer infection to the new host. Between 5% and 10% of HTLV-1-infected individuals develop ATL or inflammatory diseases. STD, sexually transmitted disease.