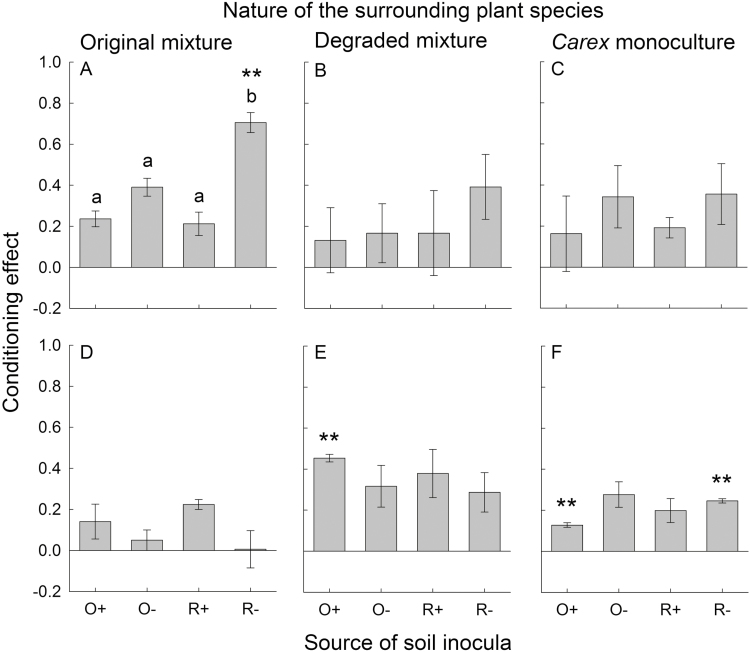
Figure 2.
Effect of soil conditioning on Carex (upper row; A–C) and surrounding plant species (lower row; D–F) when grown in soil originating from different field types. The conditioning effect (mean ± SE) was calculated as ln [(total biomass when grown in soil conditioned with a mixture of plants characteristic of original fen meadows)/(total biomass when grown in soil conditioned with a mixture of plants characteristic of degraded fen meadows)]. The soil inoculum originated from four field types: original with characteristic fen meadow vegetation (O+), original, but with degraded vegetation (O−), successfully restored to characteristic fen meadow vegetation (R+) and unsuccessfully restored (R−). The plants used as surrounding neighbours were: a mixture of plants characteristic of original fen meadows (A, D), a mixture of plants characteristic of degraded fen meadows (B, E) and the same plant species (Carex monoculture; C, F). Asterisks indicate a significant difference from zero (n = 3 species averages; **P < 0.01 remaining significant after control of false discovery rate). Different letters indicate significant differences among the field types within a neighbour plant mixture.