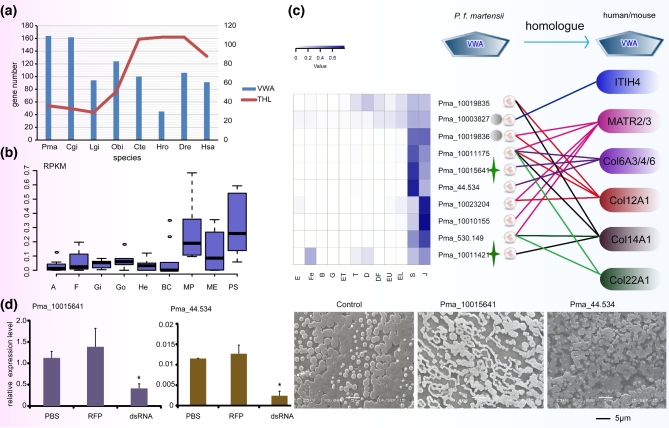
Figure 2:
Expression and functional analysis of VWAPs in P. f. martensii. (a) Number of VWAPs and THR-containing proteins in different species. P. f. martensii (Pma), C. gigas (Cgi), L. gigantea (Lgi), O. bimaculoides (Obi), C. teleta (Cte), H. robusta (Hro), D. rerio (Dre), and H. sapiens (Hsa). (b) Expression of 10 genes encoding VWAPs from nacreous shell matrix showing higher expression in the MP and PS than in other organs. The y-axis is the normalized RPKM value. The x-axis lists 9 organs/tissues (MP: mantle pallium; ME: mantle edge; A: adductor muscle; He: hepatopancreas; BC: hemocyte; Go: gonad; Gi: gill; F: foot; PS: pearl sac at 180 days after nucleus transplantation). (c) Expression pattern of the 10 VWAPs during early development and the homology of their VWA domains to that from human and mouse proteins. E: egg; Fe: fertilized egg; B: blastula; G: gastrula; ET: early trochophore; T: trochophore; D: D-stage larvae; DF: D-stage larvae before feeding; EU: early umbo larvae; EL: eyed larvae; S: spat; J: juveniles. (d) Expression of Pma_10015641 and Pma_44.543 and nacre growth after RNA interference. Left: relative expression of Pma_10015641 and Pma_44.534 in mantle after RNAi; PBS: control; RPF: red fluorescent protein; dsRNA: RNAi. Right: Disordered microstructure of nacre observed after inhibition of the 2 VWAP genes (bar = 5 μm). Col: collagen; ITIH4: inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4; MATR: matrilin.