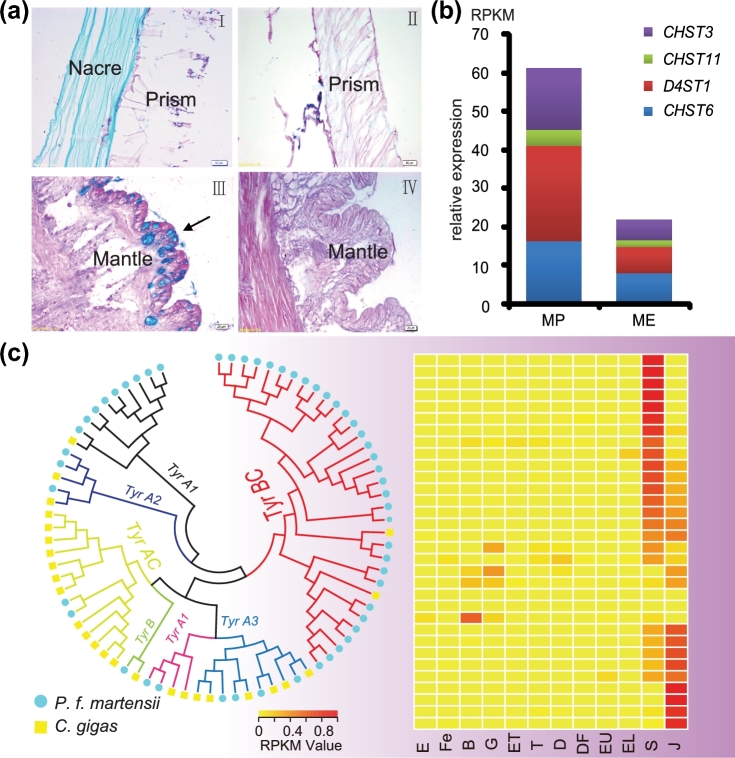
Figure 3:
GAGs and tyrosinase genes in P. f. martensii. (a) The shell matrix extracted from the nacre of P. f. martensii contains abundant acid glycosaminoglycans stained blue (I), whereas matrices extracted from the prismatic layer of P. f. martensii (I) and C. gigas (II) contain neutral GAGs stained red. Secretory cells (arrow) in the mantle pallium of P. f. martensii are filled with acid GAGs stained blue (III), whereas cells in the mantle pallium of C. gigas contain neutral GAGs stained red (IV). (b) Expression (y-axis) of CHST3, CHST11, CHST6, and D4ST1 in the mantle pallium and the mantle edge. (c) Phylogenetic tree of tyrosinase proteins from P. f. martensii and C. gigas. Tyrosinase genes specifically expanded in P. f. martensii are shaded in purple, and their expression patterns during early development are presented in the heat map. E: egg; Fe: fertilized egg; B: blastula; G: gastrula; ET: early trochophore; T: trochophore; D: D-stage larvae; DF: D-stage larvae before feeding; EU: early umbo larvae; EL: eyed larvae; S: spat; J: juveniles.