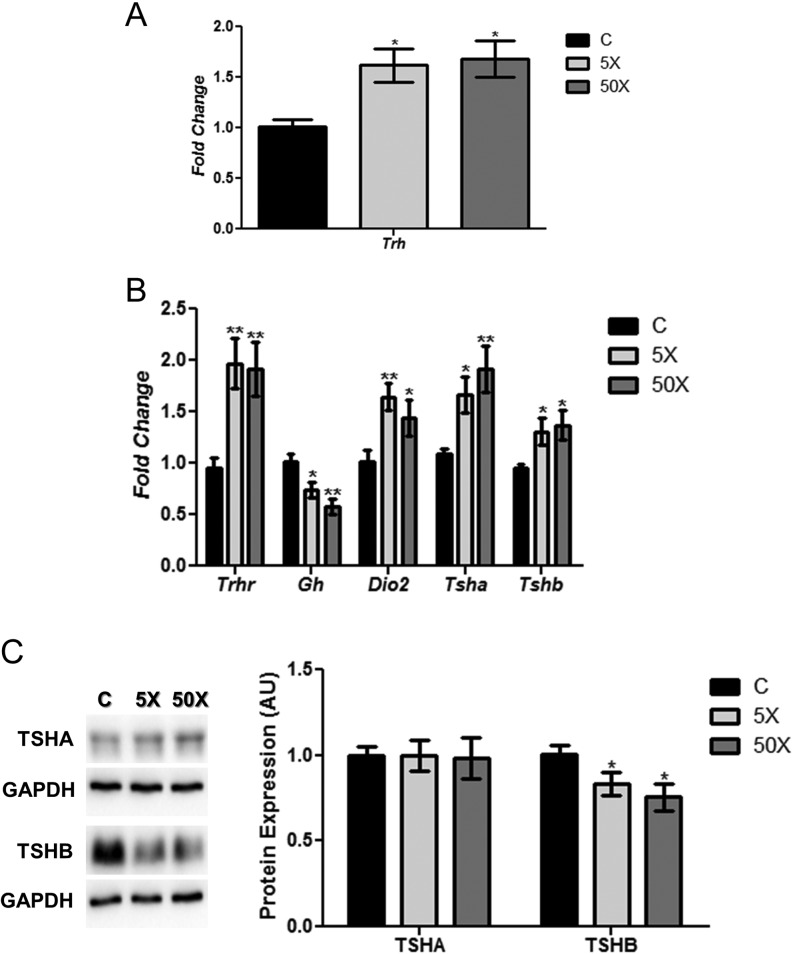
Figure 2.
Maternal IE exposure alters gene expression in the hypothalamus and the pituitary. Rat dams received distilled water (Control Group; C); distilled water supplemented with 0.6 mg/L (iodine excess group; 5×) or distilled water supplemented with 7.3 mg/L (iodine excess group; 50×) throughout pregnancy and lactation. Thereafter, hypothalamic Trh mRNA content (A) and pituitary Trhr, Gh, Dio2, Tsha and Tshb mRNA contents (B) were analyzed by Real-Time PCR and normalized to Rpl19 mRNA content. Total pituitary TSHA and TSHB protein content (C) were analyzed through Western blotting analysis, using GAPDH as loading control. Results are expressed as means ± s.e.m. as fold change or arbitrary units (AU) (n = 10–12/group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs C (ANOVA, Student–Newman–Keuls).

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a