Figure 7.
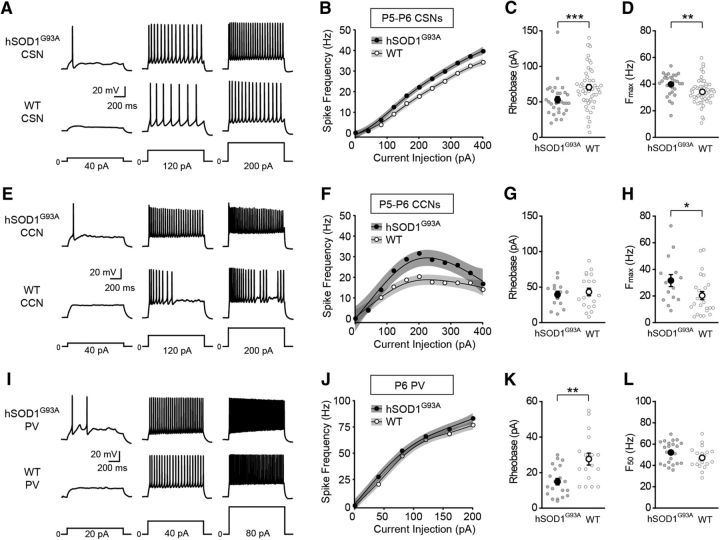
Cortical neurons are hyperexcitable in neonatal hSOD1G93A mice. A, E, Representative voltage traces recorded from CSNs (A) and CCNs (E) neurons from neonatal hSOD1G93A;Rbp4-Cre;tdTomato (hSOD1G93A) and Rbp4-Cre;tdTomato (WT) mice evoked by 40, 120, and 200 pA current steps. B, F, The current–spike frequency relationship measured from CSNs (B; P5–P6; hSOD1G93A, n = 29 cells from 9 mice; WT, n = 53 cells from 10 mice; p < 1.13 × 10−12, Wald test,) and CCNs (F; P5–P6; hSOD1G93A, n = 15 cells from 5 mice; WT, n = 24 cells from 8 mice; p < 1.82 × 10−6, Wald test,) from neonatal hSOD1G93A and WT mice. C, G, The rheobase measured from CSNs (C; hSOD1G93A, 53.03 ± 4.48 pA; WT, 70.55 ± 3.93 pA; p = 0.0008, Mann–Whitney test) and CCNs (G; hSOD1G93A, 39.43 ± 4.71 pA; WT, 43.2 ± 5.15 pA; p = 0.7123, Mann–Whitney test). D, H, The Fmax measured from CSNs (D; hSOD1G93A, 39.79 ± 1.5 Hz; WT, 34.17 ± 1.31 Hz; p = 0.0017, Mann–Whitney test) and CCNs (H; hSOD1G93A, 31.56 ± 4.51 Hz; WT, 20.31 ± 3.04 Hz; p = 0.0293, Mann–Whitney test). I, Representative voltage traces recorded from PV interneurons from neonatal hSOD1G93A;Gad67-GFP;Rbp4-Cre;tdTomato (hSOD1G93A) and Gad67-GFP;Rbp4-Cre;tdTomato (WT) mice evoked by 20, 40, and 80 pA current steps. J, The current–spike frequency relationship for PV neurons from hSOD1G93A and WT neonatal mice (P6; hSOD1G93A, n = 23 cells from 11 mice; WT, n = 19 cells from 7 mice; p < 0.00556, Wald test). K, The rheobase measured from PV interneurons (hSOD1G93A, 14.9 ± 1.81 pA; WT, 27.65 ± 3.37 pA; p = 0.0028, Mann–Whitney test). L, The F50 measured from PV interneurons (hSOD1G93A, 52.11 ± 2.13 Hz; WT, 47.12 ± 2.31 Hz; p = 0.1415, Mann–Whitney test).