Fig. 2.
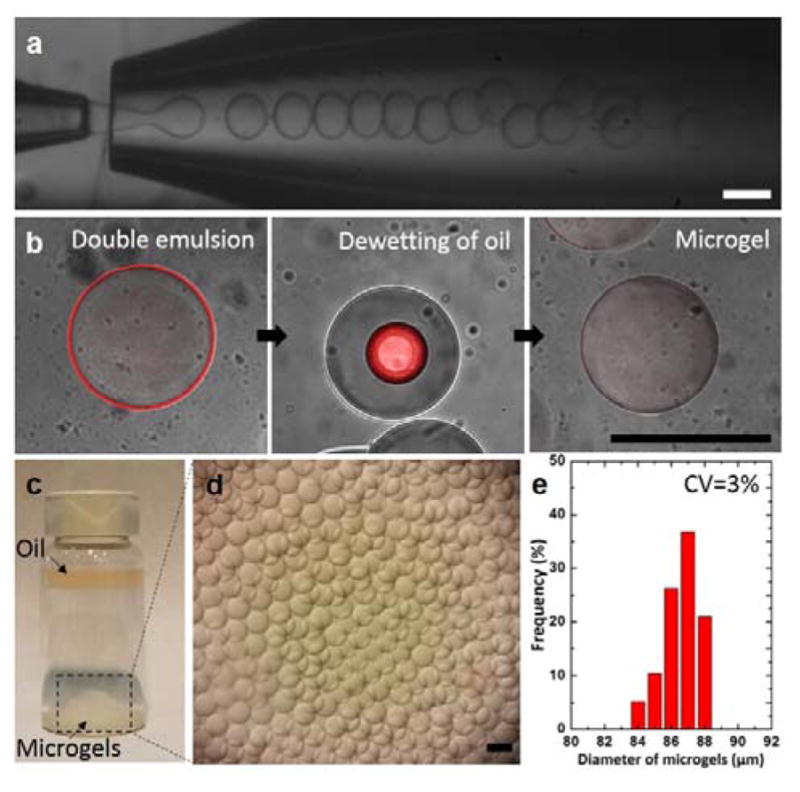
Monodisperse microgels produced by glass capillary microfluidic device. (a) Optical images showing continuous formation of double emulsion drops in a dripping mode. (b) A series of confocal images showing dynamic behavior of the oil layer as the polymerized drops are transferred in an aqueous solution (DI water). Estimated thickness of the oil shell is approximately 1 μm using image analysis. (c–d) Optical images showing the resulting microgels on the bottom surface and the oil layer collected on the top surface after the dewetting process. (e) Size distribution of the resulting microgels. All scale bars represent 100 μm.
