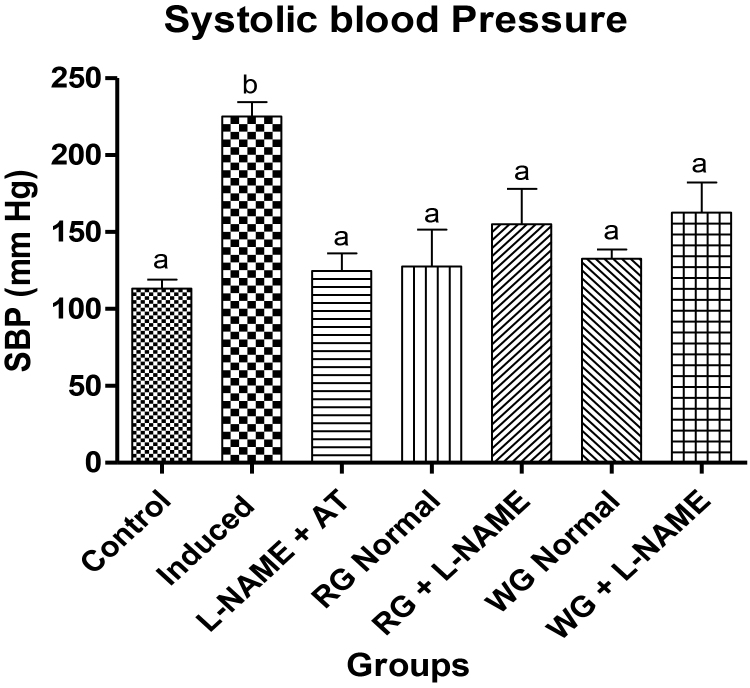
Fig. 1.
Effects of dietary supplementation of turmeric and ginger on the final systolic blood pressure (SBP) measurements in control and L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats. Data are presented as mean + SEM (n = 10). Bars with different letters are statistically different (p < 0.05). Control: Normotensive control rats placed on basal diet; Induced: Hypertensive rats placed on basal diet; L-NAME + AT: Hypertensive rats placed on basal diet + atenolol (10 mg/kg/day); RG Control: Normotensive rats placed on basal diet supplemented with 4% turmeric; RG + L-NAME: Hypertensive rats placed on basal diet supplemented with 4% turmeric; WG Control: Normotensive rats placed on basal diet supplemented with 4% ginger; WG + L-NAME: Hypertensive rats placed on basal diet supplemented with 4% ginger.