Table 1.
Identification of Optimal Reagent for Cycloguanidylationa
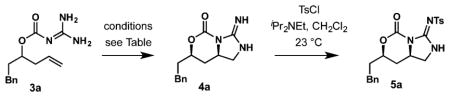
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| entry | reaction conditions | conversion (%) | yield (%) |
| 1 | 10 mol % Pd(OAc)2, CuI, K2CO3, DMF, 23 °C, 24 h | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 25 mol % Pd(OAc)2, PhI(OAc)2, CH2Cl2, 23 °C, 24 h | 15 | 0 |
| 3 | 5 mol % Pd(OAc)2, PhI(OAc)2, NMe4Cl, NaOAc, CH2Cl2, 23 °C, 24 h | 30 | 0 |
| 4 | 10 mol % NiCl2, PhI(OAc)2, NaOAc, DMF, 23 °C, 24 h | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 10 mol % CuI, K2CO3, 10 mol % 2,2′-bipyridine, O2, DMF, 60 °C, 24 h | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 3 equiv of t-BuOCl, CH2Cl2, 0 °C, 20 min | 100b | 0 |
| 7 | Py2IBF4, toluene, 23 °C or reflux, 24 h | 65 | 0 |
| 8 | 2.1 equiv of I2, NaHCO3, CH2Cl2, 23 °C, 6 h | 15 | 0 |
| 9 | 2.1 equiv of NIS, NaHCO3, CH2Cl2, 23 °C, 1 h | 100 | 62 |
| 10 | 2.1 equiv of NIS, NaHCO3, CH3CN, 0 °C, 5 h | 100 | 84 |
See Supporting Information for additional details; isolated yields of 5a after tosylation are reported. Conversion measured by 1H NMR analysis of a crude mixture of products.
Dichloroguanidine is isolated.
