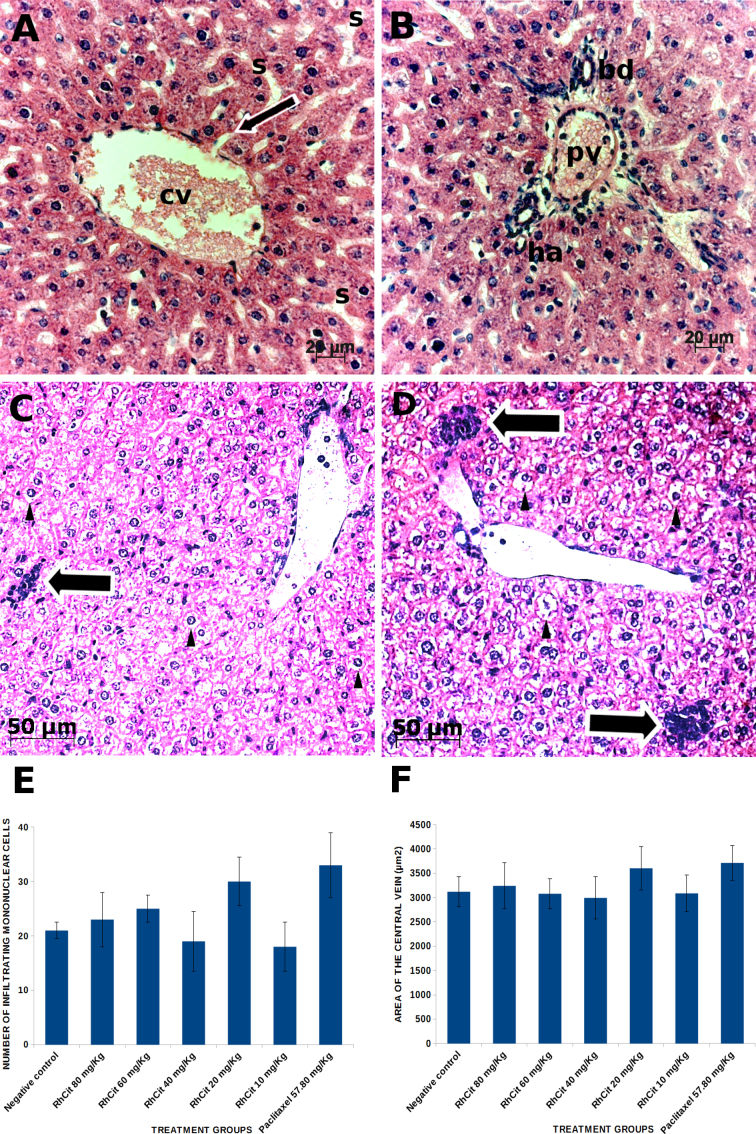
Fig. 7.
Histological sections of liver from Balb/C mice treated with rhodium (II) citrate at various concentrations. Morphology remained unaltered after administration of any of the tested dosages. Therefore, unless otherwise stated, photomicrographs are representative of all experimental groups. (A) Central vein (cv) surrounded by cords of hepatocytes radially arranged; the thin arrow indicates one of the sinusoids (s) opening into the central vein. (B) Portal area comprising branches of the portal vein (pv), hepatic artery (ha) and bile duct (bd). Vacuolation of hepatocytes (arrow head) was occasionally observed in a few lobules both in the negative control (C) and in all treatment groups (D) and was associated to the presence of infiltrating mononuclear cells (large arrows), which were counted in 12 randomly analyzed microscopic fields. No significant differences in the numbers of these cells were detected among all groups (E). Similarly, central vein area was not significantly changed after any of the treatments as compared to the negative control (F). Data are presented as mean ± SEM (standard error of mean).