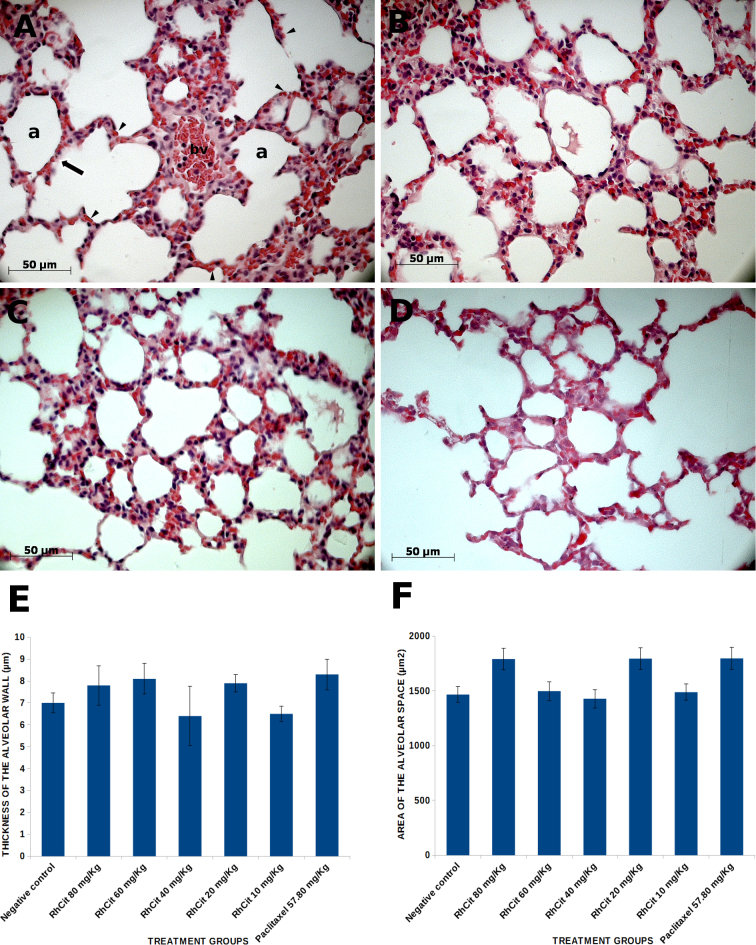
Fig. 8.
Histological sections of lung from Balb/C mice treated intraperitoneally with rhodium (II) citrate at various concentrations. Morphology remained unaltered after administration of any of the dosages. (A) Alveoli of a control animal with a blood vessel (bv) containing several erythrocytes and some mononuclear cells; erythrocytes are also visible circulating through capillaries (arrowheads) within the alveolar septum (arrow) which surrounds each alveolus (a). The same pattern of alveoli was observed in mouse treated with 80 mg/kg rhodium (II) citrate (B), which is representative of all other rhodium treatments, and paclitaxel (C). Some areas with a slight reduction in the alveolar wall (septum) thickness were equally seen both in control and treated animals (D). This parameter was assessed in 10 randomly analyzed mice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (standard error of mean).