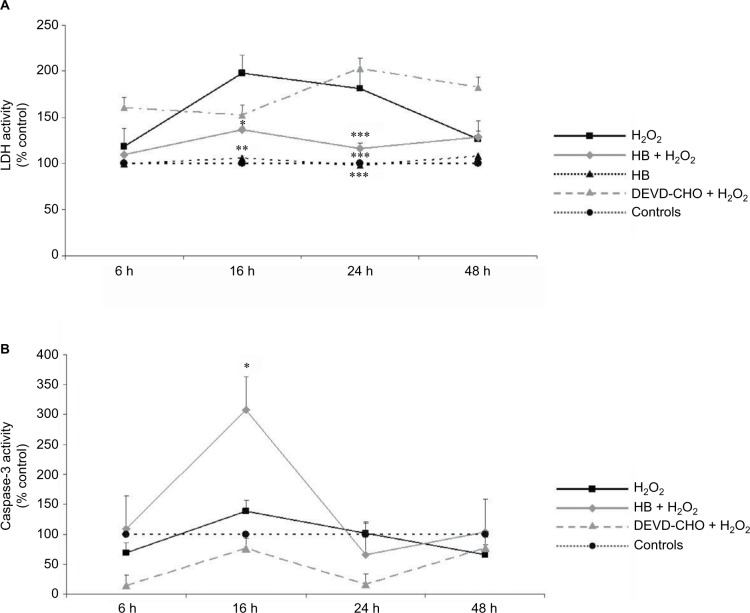
Figure 1.
HB treatment induces apoptosis after H2O2-induced oxidative stress.
Notes: (A) LDH release into the medium: H2O2 treatment induced cell death as demonstrated by high LDH release starting from 16 h; HB had a protective effect, and LDH release was reduced. The pretreatment with DEVD-CHO did not affect LDH release in H2O2-treated cells, indicating that H2O2 triggered necrotic cell death. The results are expressed as the percentage of viable cells compared with negative control cells (not treated with HB or H2O2) referred to as 100%. (B) Caspase-3 activity: HB treatment activated caspase-3, while H2O2 alone did not. Negative control cells are referred as 100%. Data are given as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA (n = 3). Significantly different from H2O2-treated cells (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001).
Abbreviations: HB, hyaluronic acid and butyric acid; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; DEVD-CHO, N-acetyl-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-aldehyde; SEM, standard error of the mean; ANOVA, analysis of variance.