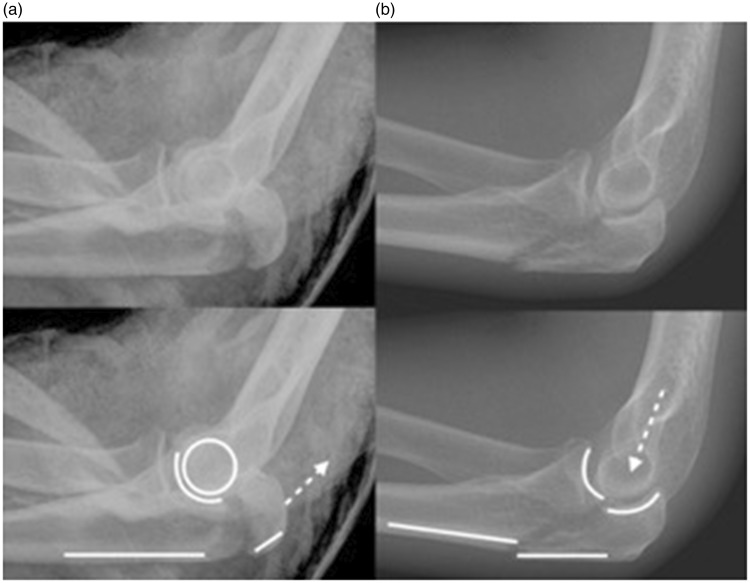
Figure 1.
(a) A typical transverse olecranon fracture treated using the suture technique. There is no translation of the dorsal cortex of the ulna and the ulnohumeral joint is congruent. The direction of force (dotted arrow) is in the line of the triceps. (b) Ulnohumeral instability following an olecranon fracture. Note the ulnohumeral incongruity and step in the dorsal cortex of the ulna created by translation of the proximal fragment relative to the ulna shaft. The dotted arrow indicates the direction of force. Plate fixation is advocated for this fracture.