Figure 1.
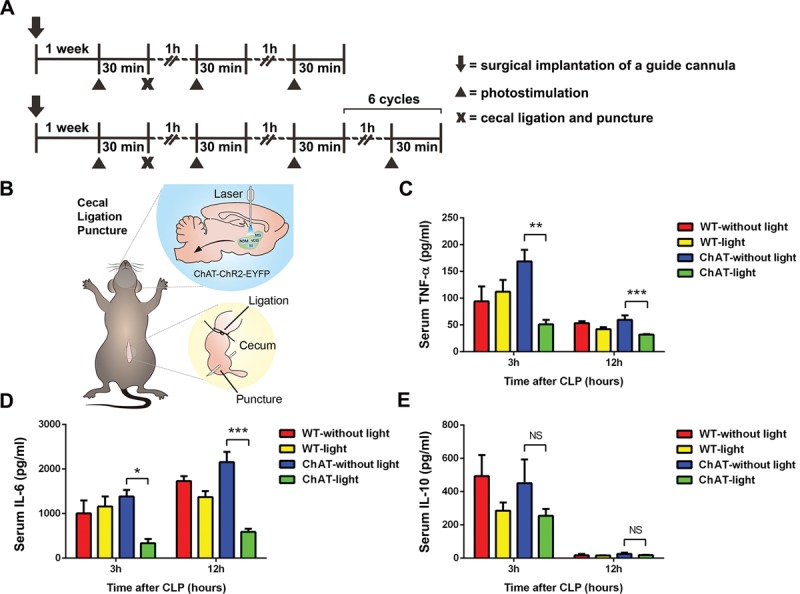
Selectively activating basal forebrain cholinergic neurons attenuated the systemic inflammatory response to cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)–induced sepsis. After photostimulation of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons and CLP surgery, blood was collected at 3 and 12 hr (n = 6–10 per group). A, The model of experiment protocol. B, Schematic drawing shows the detailed methods of photostimulation and CLP. C–D, The pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-6 were present at lower levels in photostimulated ChAT septic mice. E, There was no significant difference in the levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10) between ChAT-lit septic mice and ChAT-unlit septic mice. These data are presented as the mean ± sem (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). NS = no significant difference, WT = wild type.
