Figure 5.
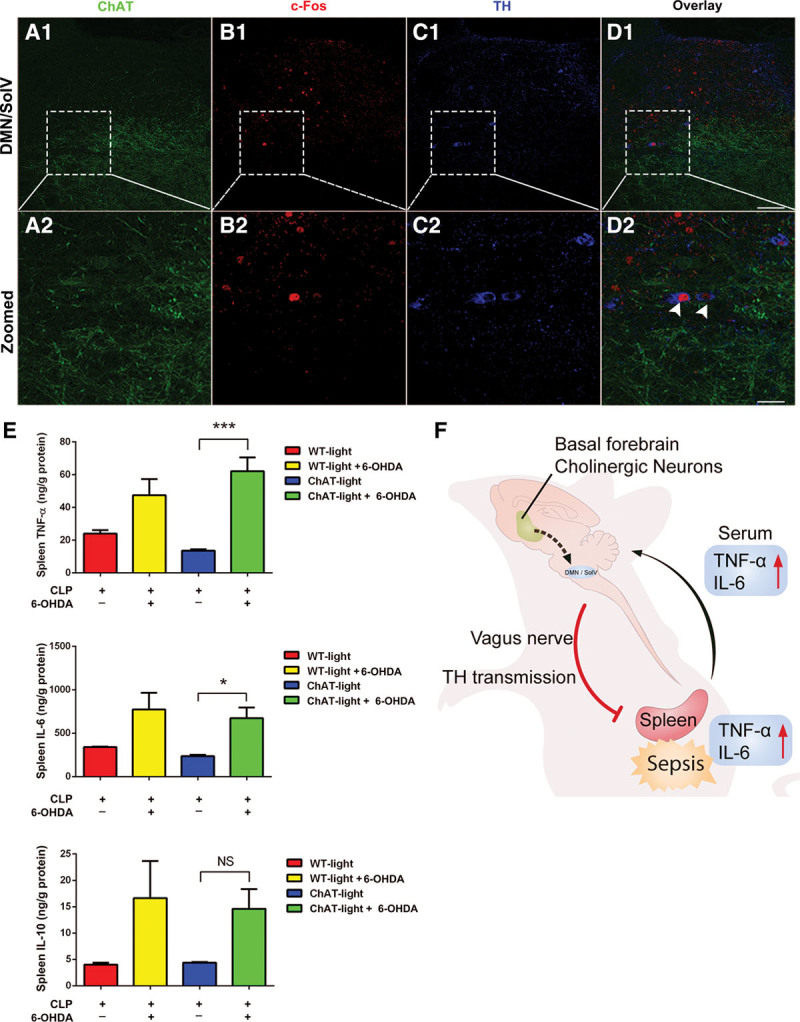
TH positive dopaminergic neurons occupy 35.2% of c-Fos–positive neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (DMN)/ventral part of solitary nucleus (SolV) activated by photostimulation of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons, and dopaminergic neurotransmission from the DMN/SolV to the spleen via vagus nerve is indispensable for the cholinergic activation–induced anti-inflammation. A1–D1, TH positive dopaminergic neurons occupy 35.2% of the c-Fos–positive neurons in the DMN/SolV. A2–D2, Serial image projection. Some c-Fos–positive neurons in the DMN/SolV were TH+ (arrows in D2). Two arrowheads indicated two example neurons expressing TH+ (blue) and c-Fos+ (red). Scale bar equals 50 μm. E, In ChAT mice, photoactivation reduced concentrations of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-6 in the spleen, and this effect was nearly completely reversed by injecting 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA). These data are presented as the mean ± sem (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). F, Schematic model on the central and peripheral pathway of neuroimmune interaction: from activation of cholinergic neurons in basal forebrain to dopaminergic neurons in DMN/SolV via vagus nerve to the spleen in sepsis. CLP = cecal ligation and puncture, NS = no significant difference, WT = wild type.
