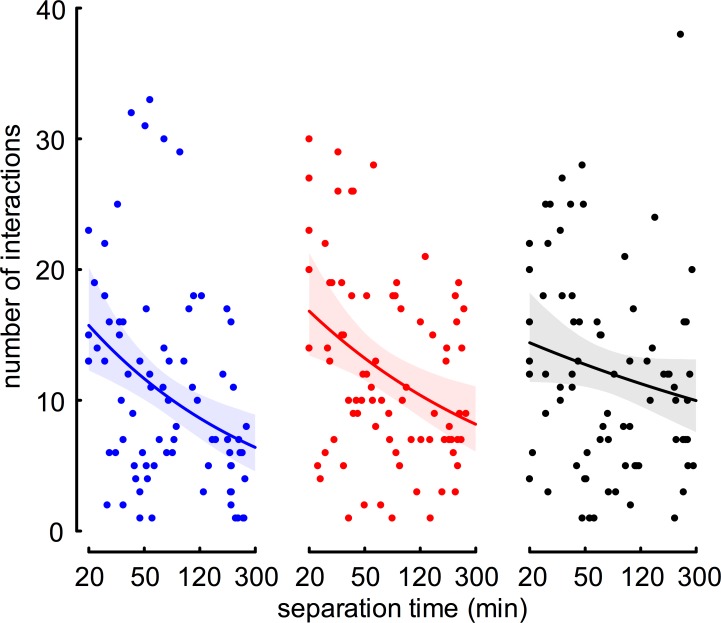
Fig 3. Effect of separation time (min) on number of interactions.
In two of the groups (social-FW vs NM in blue: -28% and social-FW vs NNM in red: -24%), the number of interactions decreases significantly with increasing separation time. For the group of isolated-FW vs NNM (black: -13%), this decrease is lower and statistically not significant different from no change. Dots represent independent measures of number of interactions. Solid lines represent fitted values from model I and shaded areas represent the 95% credible intervals of Bayesian statistics.