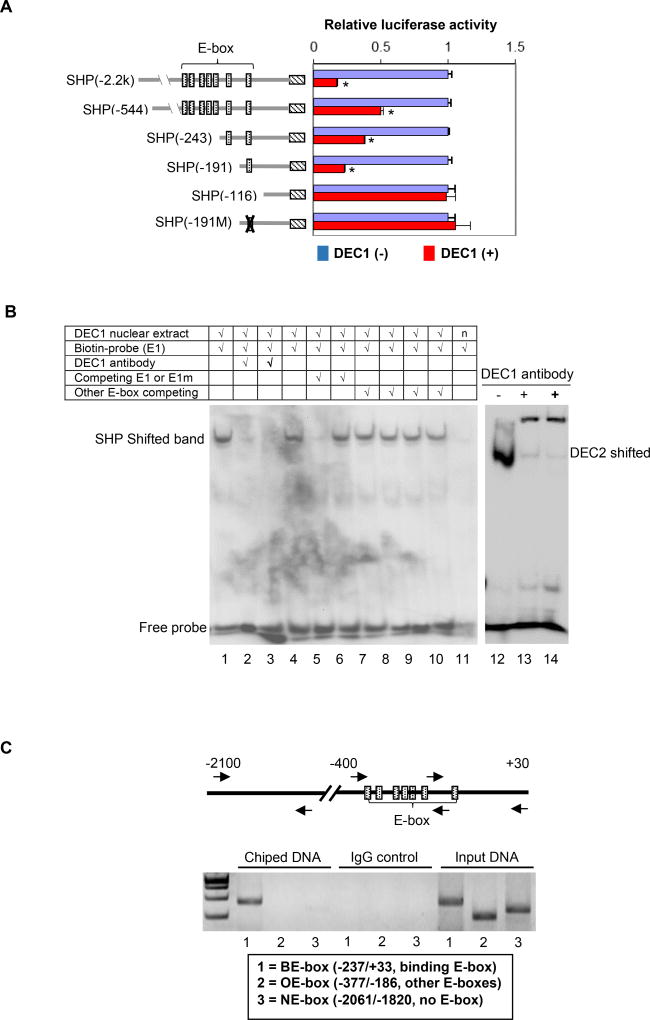
Fig. 2. Identification and characterization of the E-box element in DEC1 binding.
(A) Identification of the E-box element in DEC1 binding DEC1 stably transfected cells were cultured in the absence or presence of tetracycline (0.1 µg/mL) to modulate the expression of DEC1 (tetracycline inducible) for 24 h. The cells were then transfected with a reporter construct (50 ng), the pRL-null Renilla (5 ng) and DEC1 (0–100 ng). The reporter constructs contained the 5’ sequence of the SHP promoter at different length or a sequence with a disrupted E-box element. The transfected cells were cultured, collected and analyzed for luciferase activity as described above. Once again, the firefly luminescence signal was normalized based on the Renilla luminescence signal. The signal in the absence of DEC1 was recoded as 100% for each reporter. The asterisk sign indicates statistical significance from vector control [labeled as DEC1(−)] over DEC1 (p<0.01). (B) EMSA analysis DEC1-stably transfected cells were cultured in the absence or presence of tetracycline (0.1 µg/ml) for 24 h, and the nuclear extracts were isolated. For EMSA, nuclear extracts (5 µg) were incubated with a biotinylated 187/162 (E1) probe for 20 min. In the competition assay, nuclear extracts were pre-incubated with the unlabeled element (50×) or oligonucleotides containing another E-box (not the same as the probe) for 30 min, and then incubated with the biotinylated probe. In the disruption assay, nuclear extracts were incubated first with an antibody against DEC1 on ice for 20 min and then with the biotinylated probe. Nuclear extracts (labeled as “n”) from cells cultured without tetracycline were used as a control (right lane of the left panel). For comparison, a probe derived from DEC2, known to interact with DEC1, was included. The protein-DNA complexes were electrophoretically resolved, transferred to a Biodyne® nylon membrane and located with streptavidin-conjugated horseradish peroxidase and chemiluminescent substrate. (C) ChIP analysis HepG2 cells were transfected with DEC1 (Flag-tagged) for 24 h, washed and underwent cross-linking for 15 min by 1% formaldehyde, and the cross-linking was terminated with 125 mM glycine. Alternatively DEC1 stably transfected cells were cultured in the presence of tetracycline (0.1 µg/ml) for 24 h and then processed as described for HepG2 cells. The soluble chromatins were prepared, pre-cleared with protein G beads and incubated with a Flag antibody (HepG2) or anti-DEC1 (stably transfected cells). As a control, the antibody was replaced with pre-immune IgG. The antibody-bound chromatins, DNA input (1/20 of the antibody-bound chromatins) as well as IgG-control were analyzed by PCR for the presence of the genomic fragment containing the E-box of interest, other E-boxes or no E-box. Both cells produced similar images and the image from HepG2 cells is shown).