Figure 2.
vHMECs Arise from HMECs Following Epigenetic Reprogramming
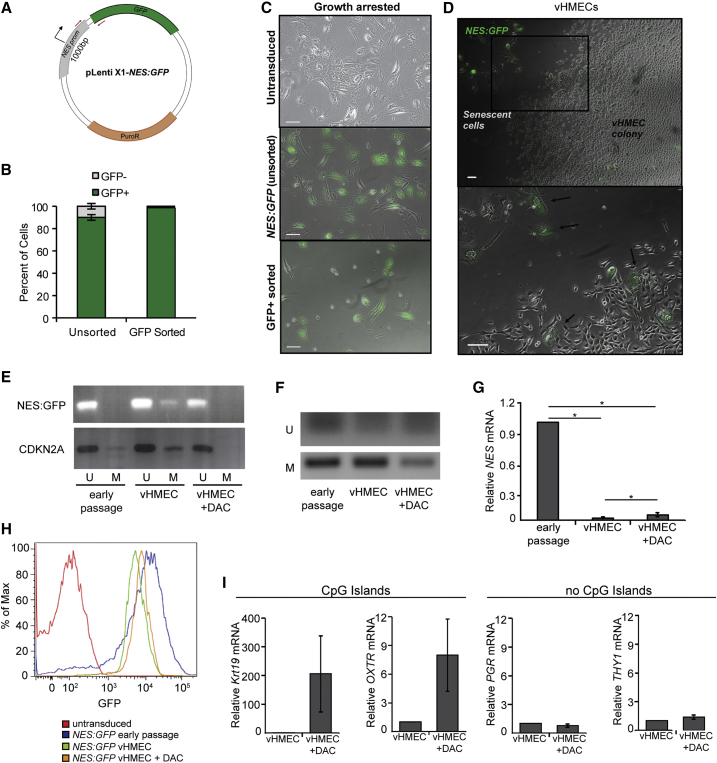
(A) Schematic of the construct used to GFP-label primary HMECs with an exogenous NES promoter; methylation-specific PCR primers are shown in red.
(B) Quantification of flow cytometry analysis of the percentage of GFP+ versus GFP− cells in HMEC cultures before and after FACS purification of GFP+ cells, n = 3.
(C) Representative images of untransduced, unsorted, and GFP+-sorted NES:GFP cultures at the point of growth arrest. The minority GFP− cells present in the unsorted cultures are absent from the FACS-purified cultures. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(D) Representative low-power (top) and high-power (bottom) images of a vHMEC colony derived from FACS-purified GFP+ cells showing GFP+ senescent cells (arrows) adjacent to GFP− vHMECs. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(E and F) Methylation-specific PCR of the (E) exogenous NES:GFP promoter, CDKN2a, or (F) endogenous NES promoter region, in early-passage HMECs, vHMECs, or in vHMECs treated with decitabine (DAC) from (E) NES:GFP or (F) untransduced cultures. U, unmethylated; M, methylated.
(G) qPCR analysis of NES expression in HMECs, vHMECs, and vHMECs treated with DAC, n = 3.
(H) Flow-cytometry analysis of high GFP expression in early-passage NES:GFP HMECs, decreased expression in NES:GFP vHMECs, and partial rescue by treatment of NES:GFP vHMECs with DAC.
(I) qPCR analysis of mammary lineage gene expression in early HMECs, vHMECs, and vHMECs treated with DAC, relative to vHMEC, n = 4.
In all panels, error bars indicated the mean ± SEM and replicates are individual patient samples. ∗p < 0.05, Student's t test.