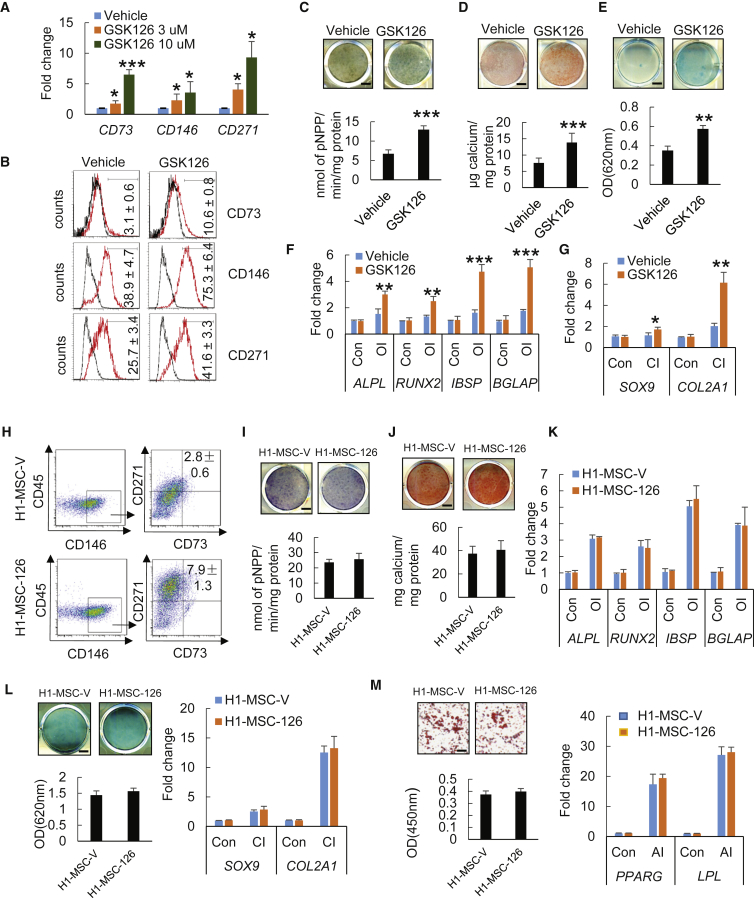
Figure 4.
Effect of GSK126 Treatment on Mesenchymal Lineage Commitment of H1 hESCs
(A) qRT-PCR gene expression analysis of well-known MSC surface markers (CD73, CD146, and CD271).
(B) Flow-cytometry analysis for CD73, CD146, and CD271 expression of cells treated with DMSO or GSK126.
(C) ALP staining and quantitative ALP activity assay after 14 days of osteogenic induction (OI) for DMSO- or GSK126-treated cells. Scale bar, 300 μm.
(D) ARS staining and quantification after 14 days of OI for DMSO- or GSK126-treated cells. Scale bar, 440 μm.
(E) Alcian blue staining and quantification after 21 days of chondrogenic induction (CI) for DMSO- or GSK126-treated cells. Scale bar, 440 μm.
(F and G) qRT-PCR gene expression analysis of osteogenic markers (ALPL, RUNX2, IBSP, and BGLAP) (F) and chondrogenic markers (SOX9 and COL2a1) (G) after lineage-specific differentiation in H1 cells treated with or without GSK126.
(H) Proportions of CD90+CD146+CD271+CD45– H1-MSC-V and H1-MSC-126 are compared.
(I) ALP staining and quantitative ALP activity assay of H1-MSC-V and H1-MSC-126 after 14 days of OI. Scale bar, 440 μm.
(J) ARS staining and quantification of H1-MSC-V and H1-MSC-126 after 14 days of OI. Scale bar, 440 μm.
(K) qRT-PCR gene expression analysis of osteogenic markers (ALPL, RUNX2, IBSP, and BGLAP) in H1-MSC-V and H1-MSC-126 after 14 days of OI.
(L) Alcian blue staining and quantification (left) and qRT-PCR gene expression analysis of chondrogenic markers (SOX9 and COL2a1) (right) of H1-MSC-V and H1-MSC-126 after 21 days of CI. Scale bar, 440 μm.
(M) Oil red O staining and quantification (left) and qRT-PCR gene expression analysis of adipogenic markers (PPARG and LPL) (right) of H1-MSC-V and H1-MSC-126 after 21 days of adipogenic induction (AI). Scale bar, 440 μm.
Data are shown as mean ± SD; n = 3 independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 by Student's t test. See also Figures S3 and S4.