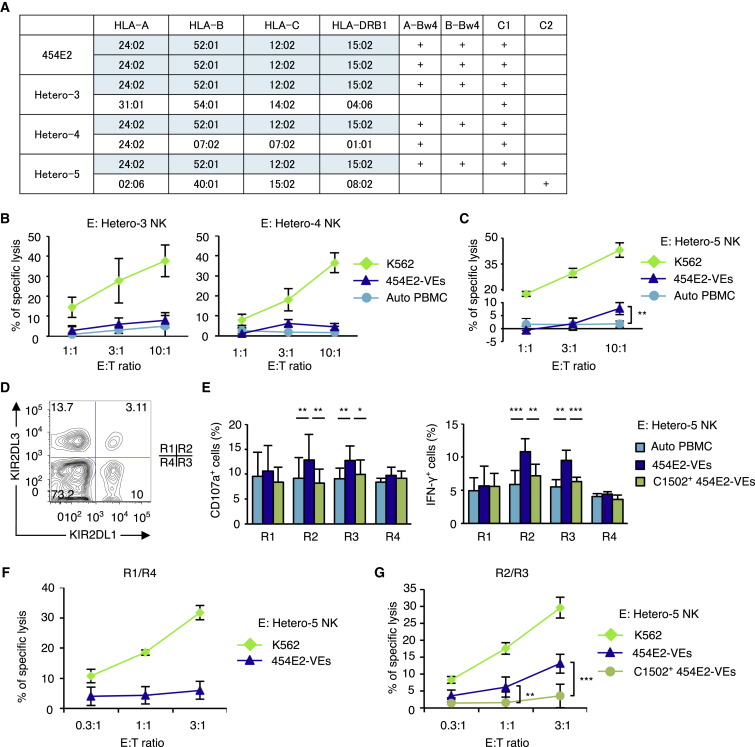
Figure 6.
KIR-Ligand-Mismatched NK Cells Respond to VE Cells Regenerated from iPSCs Homozygous for the Most Frequent HLA Haplotype in Japanese
(A) HLA haplotypes and KIR ligands of an iPSC line (454E2) and those of three blood donors. The 454E2 line is homozygous for the most frequent HLA haplotype in Japanese (shaded in blue), and the blood donors are all heterozygous for this haplotype. Note that donor Hetero-5 is the only source of NK cells that carries the group 2 HLA-C ligand, so the KIR2DL1+ NK cells are licensed only in this donor within the panel.
(B and C) Eighteen-hour cytotoxicity assay of NK cells collected from (B) Hetero-3 (C1/C1), Hetero-4 (C1/C1), and (C) Hetero-5 (C1/C2).
(D) The R1–R4 subsets within the NK cells isolated from donor Hetero-5, as defined by the heterogeneous expression of KIR2DL1 and KIR2DL3.
(E) Twelve-hour co-culture assay using NK cells isolated from Hetero-5.
(F and G) Eighteen-hour cytotoxicity assays of NK cells isolated from Hetero-5 against 454E2-VEs. The KIR2DL1-positive and -negative NK cell subsets were isolated from Hetero-5 using magnetic beads.
Results are presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, Student's t test.