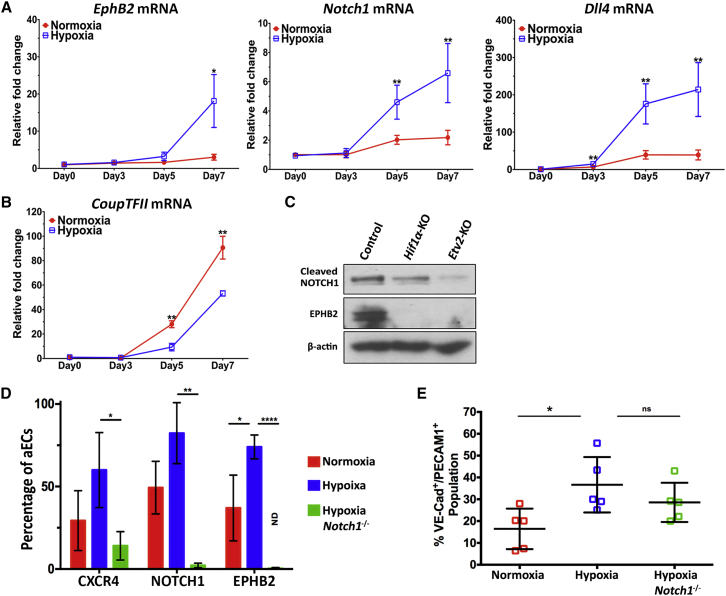
Figure 3.
HIF1α in the Second Phase Directs Differentiation of ESCs to Arterial EC Fate via NOTCH1 Signaling
(A and B) mRNA expression of arterial EC markers EphrinB2, Notch1, and Dll4, and the venous EC marker Coup-TFII on days 0, 3, 5, and 7 of EC differentiation (n = 3 independent experiments). Results show preferential generation of aECs during hypoxia as opposed to venous-type ECs.
(C) Representative immunoblot of decreased expression of arterial EC markers EPHB2 and cleaved NOTCH1 in hypoxia-differentiated Hif1α −/− and Etv2−/− mESCs (n = 4 independent experiments).
(D) Percentage of arterial ECs in the endothelial differentiated pool at day 7. ECs were sorted by surface PECAM1 expression and analyzed for aEC markers CXCR4, NOTCH1, and EPHB2. Results show that hypoxic differentiation preferentially generates aECs and Notch1 deletion ablates aEC formation (n = 3 independent experiments).
(E) Percentage of VE-cadherin+/PECAM1+ endothelial progenitors differentiated from mESCs on day 7. Results show that deletion of Notch1 in mESCs inhibit aEC formation but does not affect EC generation (n = 5 independent experiments).
Data are shown as means ± SD. ∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001; ns, not significant.