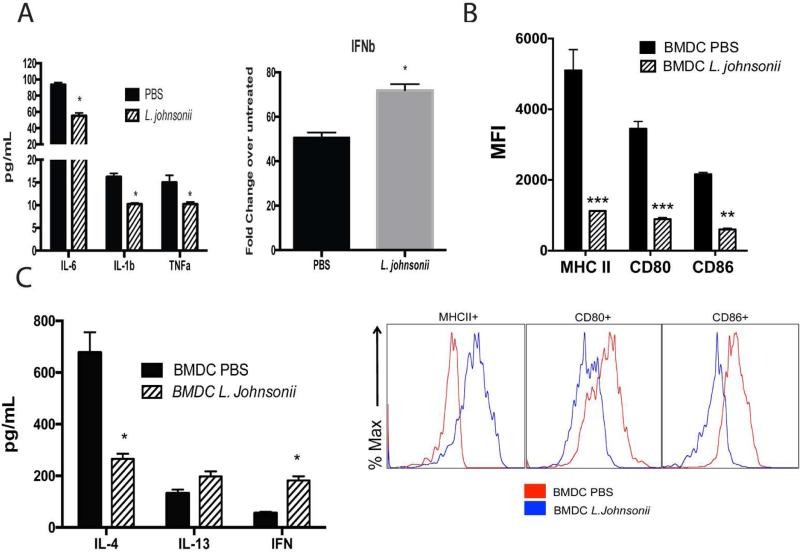
Figure 2. Bone marrow derived DC (BMDC) from L. johnsonii supplemented mice have altered inflammatory and costimulatory activity to promote an modulated T cell activation profile.
BMDC were grown from femurs of animals supplemented daily with L. johnsonii (1 × 107 cfu) or PBS by oral gavage for 7 days. BMDC were infected with RSV (MOI of 1.0) and 24 hrs. later examined for (A) mRNA expression of innate cytokines, (B) upregulation of MHC II and co-stimulatory marker expression by flow cytometry (MFI=mean fluorescence intensity), and (C) for their ability to activate T cells from lung draining lymph nodes of 8 day RSV infected wildtype mice for production of cytokines after 48 h. Data represent mean ± SE from 3 mice with 3-4 repeats. *P<0.05. ***P<0.001.