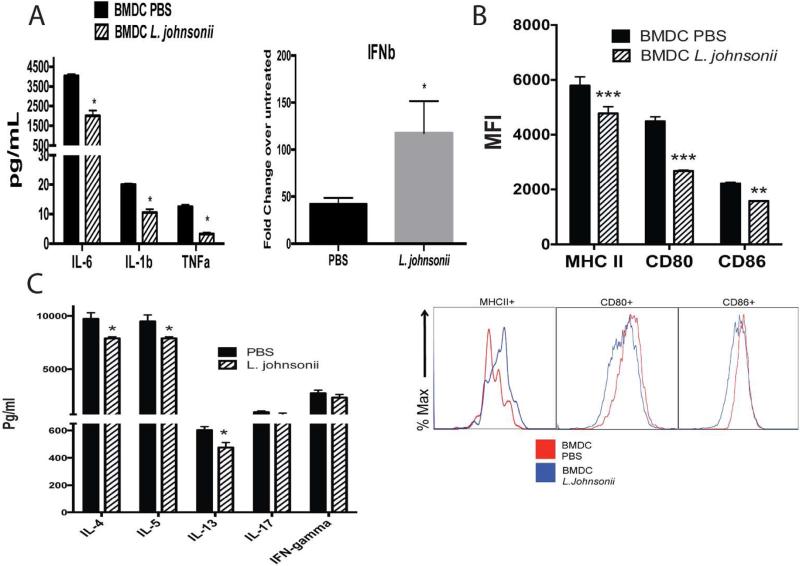
Figure 5. Plasma from L. johnsonii supplemented animals significantly alter the BMDC function compared to plasma from unsupplemented animals.
Plasma was isolated from 2 day RSV infected animals with or without a 7 day L. johnsonii supplementation prior to infection. (A) RSV-infected BMDC from wildtype mice pre-incubated with plasma for 16 h and characterized for co-stimulatory molecule expression by flow cytometry after 24 hrs. Mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) indicates the expression level of each molecule. (B) RSV-infected BMDC incubated with plasma (2%) from animals with or without L. johnsonii supplementation were combined with CD4 T cells isolated from the lung draining lymph nodes of 8 day RSV infected mice. After 48 h of activation the supernatants were assessed for T cell associated cytokine levels to determine the capacity of the DC for APC function. (C) Innate cytokine levels from RSV-infected BMDC incubated with plasma (2%) from animals with or without L. johnsonii supplementation measured after 24 hrs of infection. Data represents Mean ± SE from 3 repeats. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.005.