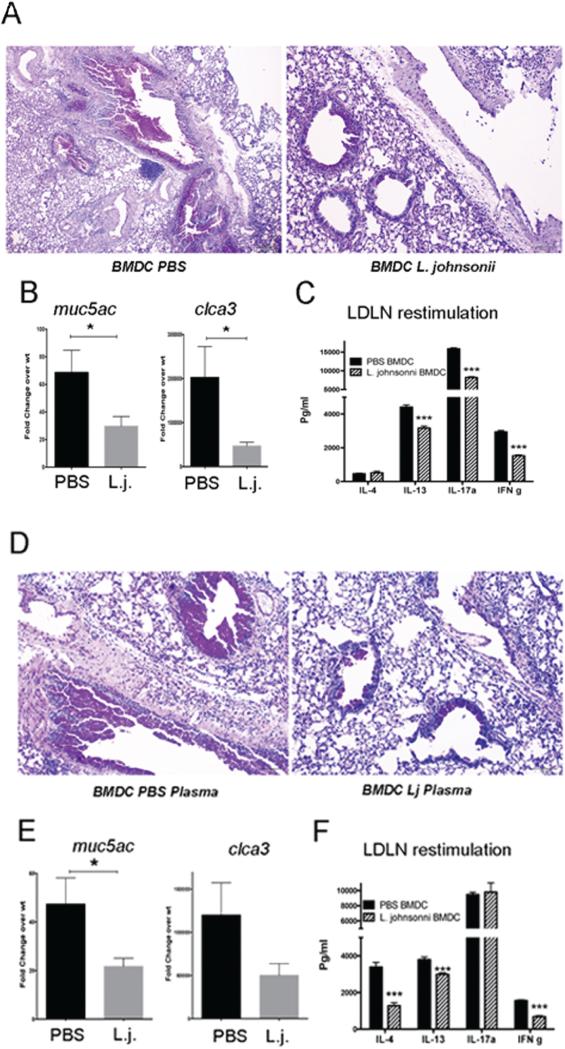
Figure 6. Adoptive transfer of BMDC from L. johnsonii-supplemented mice or those treated with plasma from supplemented animals have reduced RSV-induced pathology and altered immune responses.
RSV-infected BMDC grown from L. johnsonii-supplemented mice were transferred into the airways of naïve mice followed by RSV infection 7 days later. After an additional 8 days of infection the lungs were harvested for histologic (A) and PCR (B) analysis. In a separate study using the same protocols lung draining lymph nodes (LDLN) were restimulated by RSV for 48 h for cytokine analysis (C). In a second set of studies BMDC from wildtype mice were treated with plasma from PBS or L. johnsonii-supplemented mice and infected with RSV, followed by instillation into the airways of naïve mice 24 hrs later. Seven days later the animals were infected with RSV and harvested 8 days later, similar to the experiment in Figure 6A. The histologic assessment demonstrated reduced inflammation and mucus staining by PAS (D). The mRNA expression of muc5ac and clca3 (gob5) was assessed by QPCR (E). In a separate study, RSV-restimulated LDLN supernatants were assessed by bioplex analysis after 48 hrs of culture (F). Data represent mean ± SE from 5 mice/group. *P<0.05. ***P<0.001.