Figure 2. Major Aβ clearance pathways and the roles of apoE and apoE receptors.
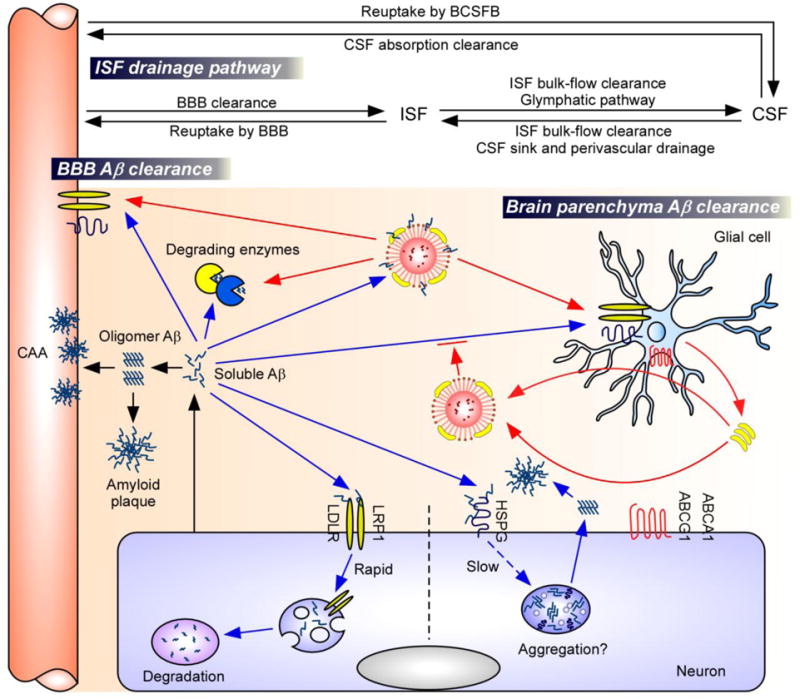
Aβ is predominantly produced by neurons (6–8). The accumulation of soluble Aβ in the brain parenchyma leads to the formation of Aβ oligomers and amyloid plaques, whereas its accumulation in the perivascular region leads to CAA (6–8). Soluble Aβ can be removed from the brain by various clearance pathways closely linked to each other: soluble Aβ in ISF can be cleared in brain parenchyma, transported to the blood through BBB, or is degraded by vascular mural cells. Aβ can also traffic along the ISF bulk flow into CSF sink where it could be absorbed into the circulatory and lymphatic systems (6, 60). Major Aβ clearance pathways include receptor-mediated clearance (e.g., LRP1, LDLR) by cells in the brain parenchyma (neurons and glia), uptake from the perivascular space by vascular mural cells, or proteolytic degradation by endopeptidases (e.g., NEP, IDE) (6–8). Binding of Aβ to neuronal HSPGs on the cell surface hinders proteolytic degradation of Aβ, and promotes Aβ oligomerization and aggregation (75). ApoE is generated mainly by the glial cells and lipidated by ABCA1 and ABCG1 transporters, forming lipoprotein particles (15). Lipidated apoE could either bind to Aβ and facilitates Aβ clearance through cell-surface receptors (e.g., LRP1, LDLR) (apoE2 > apoE3 > apoE4) (77–80). Alternatively, apoE might also suppress Aβ clearance by competing with Aβ for receptor binding in astrocytes (apoE4 > apoE3) (81).
Abbreviations: Aβ, amyloid-β; BBB, blood-brain barrier; BCSFB, blood-CSF barrier; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; ISF, interstitial fluid; CAA, cerebral amyloid angiopathy; NEP, neprilysin; IDE, insulin-degrading enzyme; LRP1, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1; LDLR, low-density lipoprotein receptor; HSPG, heparan sulfate proteoglycan; ABCA1, ATP-binding cassette A1; ABCG1, ATP-binding cassette G1.
