Figure 3.
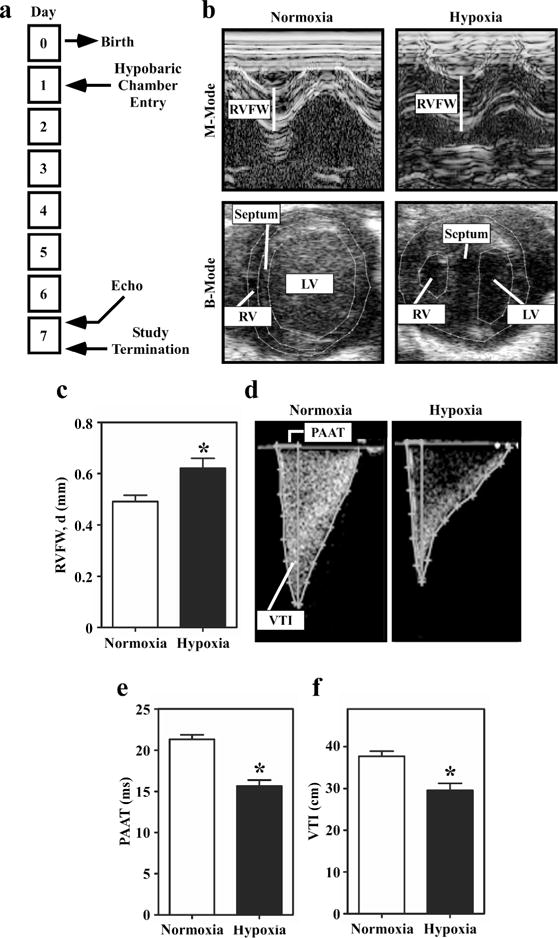
Echocardiographic analyses of right ventricular hypertrophy and pulmonary hypertension in hypoxic neonatal rats. (a) Study design. (b) Representative M-mode and B-mode images of hearts from neonatal rats exposed to hypobaric hypoxia or normoxic conditions for 7 days. (c) RV Free Wall Thickness, Diastole: Quantitative assessment of RV free wall (RVFW) thickness demonstrates increased thickness in the hypoxic rats; *P<0.05 vs. controls. (d) Representative Doppler images of pulmonary blood flow in normoxic and hypoxic neonatal rats. (e) Pulmonary artery acceleration time (PAAT) is significantly decreased in the hypoxic neonatal rats compared to control. (f) Pulmonary valve velocity-time integral (VTI) is also significantly decreased in hypoxic neonatal rats compared to control. Results are displayed as the mean with standard error. N = 11 per condition; P<0.05 vs. controls.
