Fig. 4.
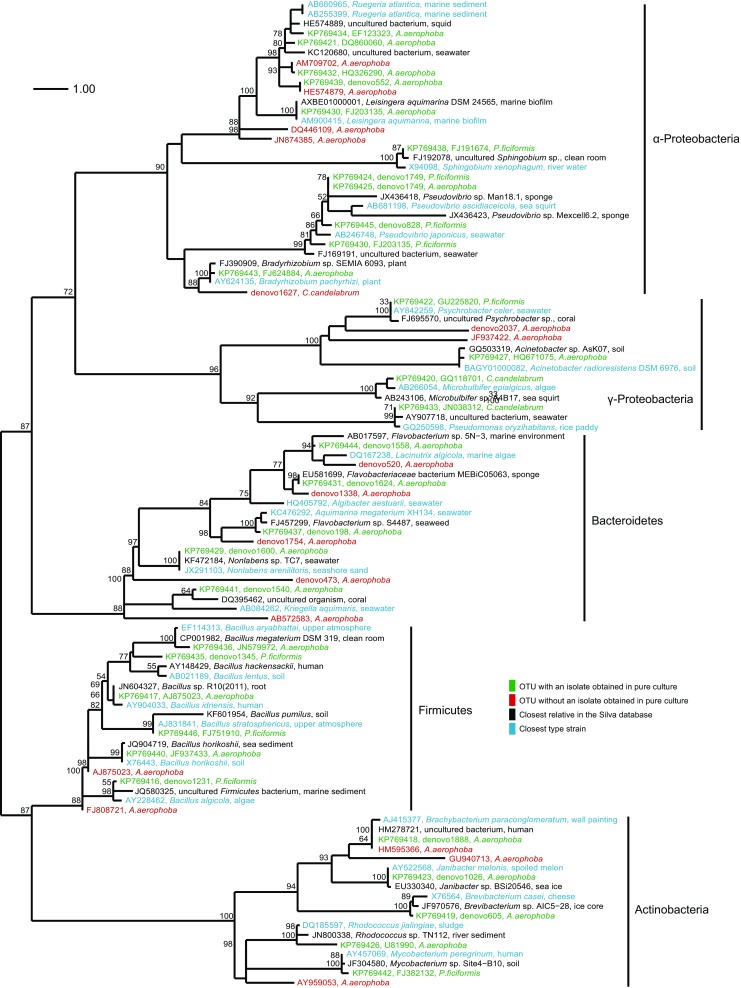
Phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity (>800-bp sequences) showing sponge bacteria cultured up to pure culture that were isolated agar media containing antibiotics (green), their closest type strain (based on blastn, blue) and the nearest neighbour in the Silva guide tree (black). The tree was constructed in ARB by maximum likelihood analysis using 1000 iterations of RAxML rapid bootstrapping. For tree calculation, highly variable positions (1–9) were excluded using the bacterial positional variability by parsimony filter, and non-overlapping regions were excluded with a custom filter (window of inclusion, positions 5331 to 26,803). For each strain, the accession number, full species name and isolation source are indicated. Bootstrap values <50 are not shown. The horizontal bar corresponds to one substitution per site. After tree creation, representative pyrosequencing reads of OTUs for which unsuccessful attempts were made to obtain a representative in pure culture (red) were added using “add species to existing tree” with ARB_Parsimony, applying similar filtering settings as those used for creation of the base tree. For these OTUs, the OTU name is stated, thereafter followed by the isolation source
