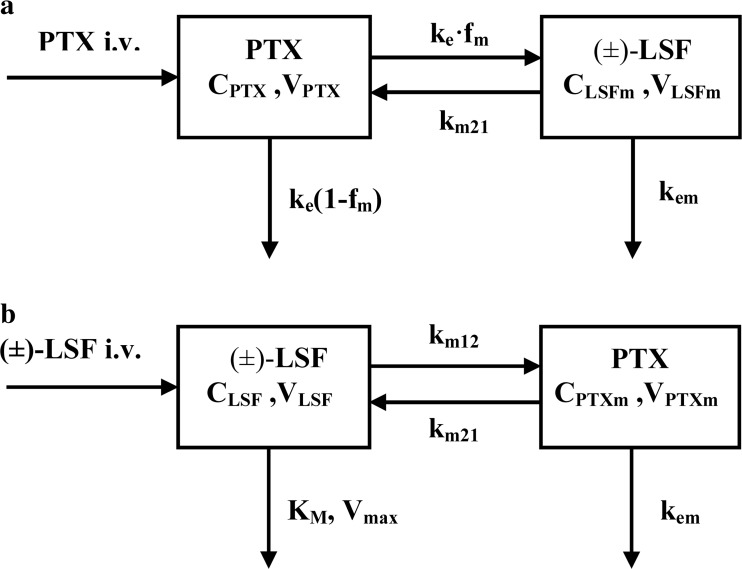
Fig. 3.
Schematic representations of the proposed pharmacokinetic models of PTX (a) and (±)-LSF (b) following intravenous administration of each compound to rats; CPTX and CLSF, plasma concentrations of PTX and (±)-LSF; VPTX and VLSF, volumes of PTX and (±)-LSF compartments, respectively; VPTXm and VLSFm, volumes of PTX and (±)-LSF metabolite compartments, respectively; km12, first-order conversion rate constant of parent compound into metabolite; km21, first-order conversion rate constant of metabolite into parent compound; ke, first-order rate constant for disappearance of parent compound; fm, fraction of parent compound metabolized; kem, first-order elimination rate constant of metabolite; Vmax, maximal elimination rate constant; Km, drug concentration at which the elimination rate is half-maximal