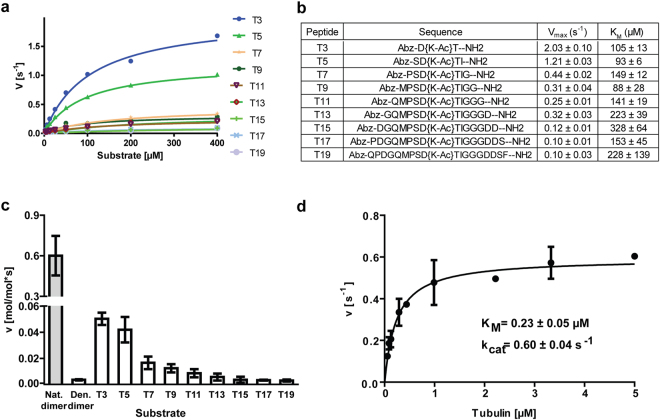
Figure 3.
Structural features outside the αK40 loop are required for efficient substrate deacetylation by HDAC6. (a,b) Michaelis-Menten kinetics for peptides derived from the Lys40 of α-tubulin (αK40) loop (3-mer to 19-mer; T3 through T19) were determined in vitro using an HPLC-based assay (a). Corresponding kinetic parameters derived from the non-linear regression fit of experimental data, together with peptide sequences, are shown in (b). High micromolar K M values indicate low affinity of HDAC6 for tested peptides, with limited contribution of residues that do not directly neighbor the central acetyllysine for the overall HDAC6 affinity/specificity. (c) Comparison of HDAC6 deacetylation rates using various substrates (natively-folded αβ-tubulin dimers, denatured tubulin dimers, peptides T3 through T19) at identical 3 μM concentrations. Deacetylation rates were determined using an HPLC assay for peptides and Western blotting quantification for tubulin dimers. Natively folded tubulin dimers are deacetylated 50- to 800-fold more efficiently than are either denatured tubulin dimers or “isolated” αK40 loop-derived peptides, suggesting that interactions/structural features outside the αK40 loop are required for efficient HDAC6/tubulin interactions. Data are presented as mean values ± s.d. (n = 3). (d) Steady-state kinetics of tubulin dimer deacetylation by HDAC6. Michaelis-Menten constants (KM and k cat) were calculated from non-linear regression fit using the GraphPad program. Data represent mean values ± s.d. (n = 3).