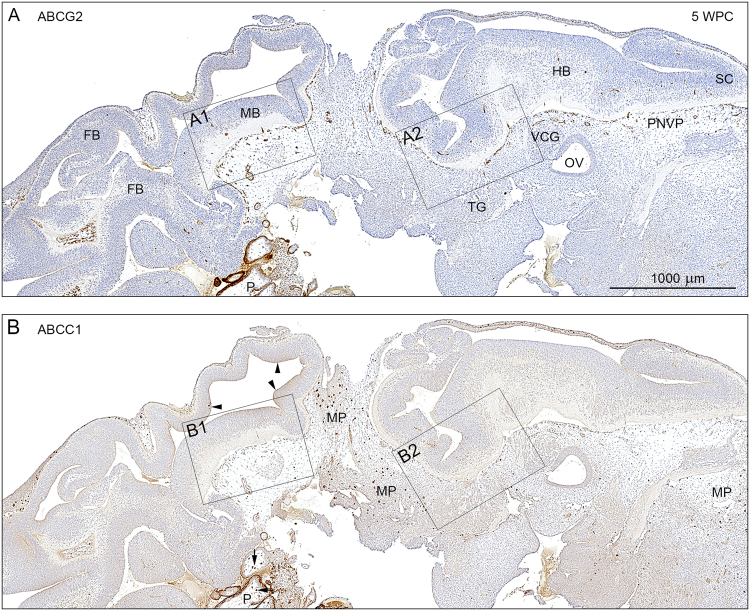
Figure 2.
Distribution of ABCG2 and ABCC1 immunoreactivity in consecutive sagittal sections of a 5 wpc human embryonic brain anlage. Immunostaining for ABCG2 (A) and ABCC1 (B) shows a dense perineural vascular plexus (PNVP) in the ventral part of the upper spinal cord (SC), the hindbrain (HB) and the midbrain (MB) but not in the dorsal forebrain, which lacks vascularization at this time. Note the many large tissue macrophages (MP) stained for ABCC1 in the loose vascular mesenchyme surrounding the brain anlage. The eCSF-brain interface is also immunopositive for ABCC1 (arrowheads in B). The boxed areas (A1, A2, B1, B2) are shown in higher magnification in Fig. 3. The specificity of the antibodies is demonstrated in placental tissue (P) included in the sections. The syncytiotrophoblastic cell layer is strongly immunopositive for ABCG2 and ABCC1, and the prominent placental stromal macrophages (Hofbauer cells) are immunopositive for ABCC1 (arrows). Abbreviations: FB: forebrain; MB: midbrain; HB: hindbrain; MP: macrophages; OV: otic vesicle; P: placental tissue; PNVP: perineural vascular plexus; SC: spinal cord; TG: trigeminal ganglion; VCG: vestibulo-cochlear ganglion, WPC: weeks post conception. (A,B) Same magnification. Scale bar: 1000 μm.