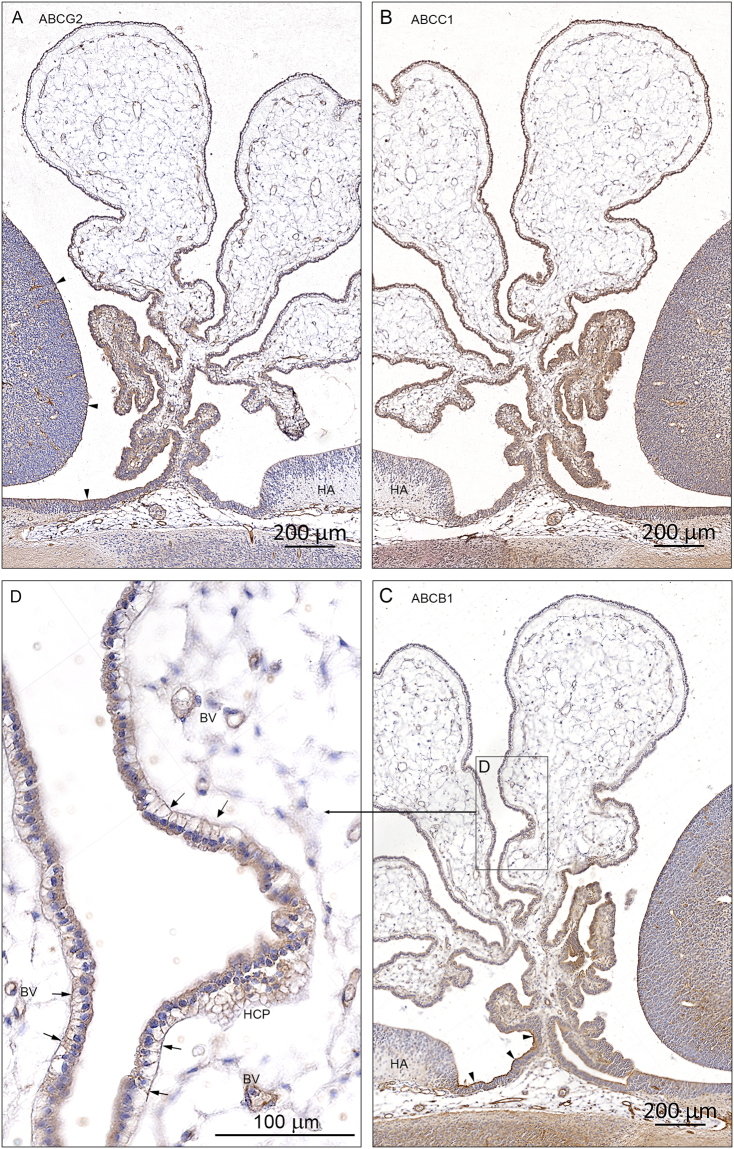
Figure 7.
Cellular distribution of ABCG2, ABCC1 and ABCB1 immunoreactivity in early lateral choroid plexus (8 wpc). Note obvious differences in the immunostaining for ABCG2 (A), ABCC1 (B) and ABCB1 (C). The root of the plexus is positively stained in both cytoplasm and along apical and basolateral membranes in all efflux transporters but the leaflets of epithelial cells leading from either the ganglionic eminence or the hippocampal anlage (HA) show a different immunoreactivity. In the ABCG2 stained section (A) there is a marked apical membrane immunoreactivity extending from the surface of the ganglionic eminence along the ganglionic leaflet (arrowheads) to the root of the plexus whereas the leaflet connecting the root with the hippocampal anlage (HA) is unstained. In the ABCC1 stained section (B) both leaflets seem to be more equally reacting. In the ABCB1-immunostained section (C) there is very strong apical membrane reactivity (arrowheads) along the leaflet connecting the root with the hippocampal anlage (HA) in contrast to the leaflet towards the ganglionic eminence. However, closer to the ganglionic eminence the surface neuroepithelial layer becomes as immunopositive as that covering the eminence. In a higher magnification of a peripheral part of the plexus (boxed area D) it is obvious that the ABCB1 immunoreactivity is most pronounced along the basolateral membranes (arrows in D) also visualized in tangential sectioned epithelium as a honeycomb pattern (HCP). Endothelial cells of the fenestrated blood vessels (BV) are also positive. Even at the low magnification in (A,B and C) it is possible to recognize positive blood vessels in the ganglionic eminences and in the subarachnoid space below the root of the choroid plexus. Abbreviations: BV: blood vessel; HA: hippocampal anlage; HCP: honeycomb pattern. (A–C) Same magnification. Scale bar: 200 μm. (D) Scale bar: 100 μm.