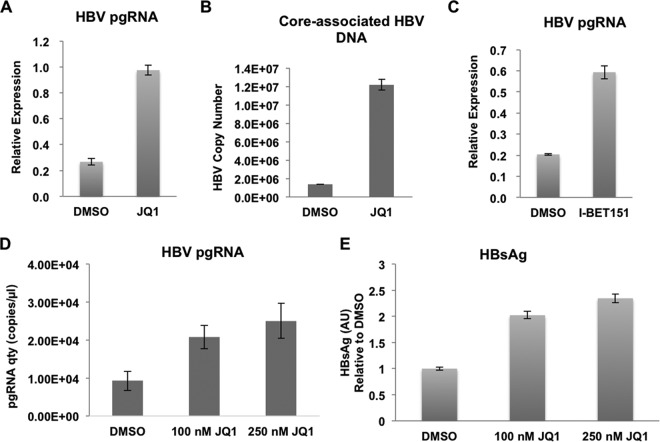
FIG 2.
Bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 activates HBV transcription and replication. (A) Treatment of HepG2.2.15 cells by JQ1 promotes HBV transcription. The levels of HBV pgRNA were assessed by RT-qPCR and normalized to the internal control GAPDH mRNA levels before and after JQ1 exposure. (B) HBV core-associated DNAs were extracted from culture medium treated with DMSO and JQ1. The DNA levels were then quantified by standard curve qPCR analysis. (C) Treatment of HepG2.2.15 cells by I-BET151 promotes HBV transcription. The levels of HBV pgRNA were assessed by RT-qPCR and normalized to the internal control GAPDH mRNA levels before and after JQ1 exposure. (D) JQ1 treatment also upregulates the transcription from the nonintegrated form of the HBV genome. Huh7 cells transiently transfected with HBV were treated with different doses (0, 100, and 250 nM) of JQ1. The levels of HBV pgRNA were then assessed by RT-qPCR and normalized to the internal control GAPDH mRNA levels. Error bars represent standard deviations from three independent measurements. (E) The surface antigen of HBV, HBsAg, is upregulated by JQ1 treatment in Huh7 cells, which were treated as described for panel B. HBsAg levels in cell culture supernatant before and after different doses of JQ1 treatment were quantified by ELISA.