FIG 6.
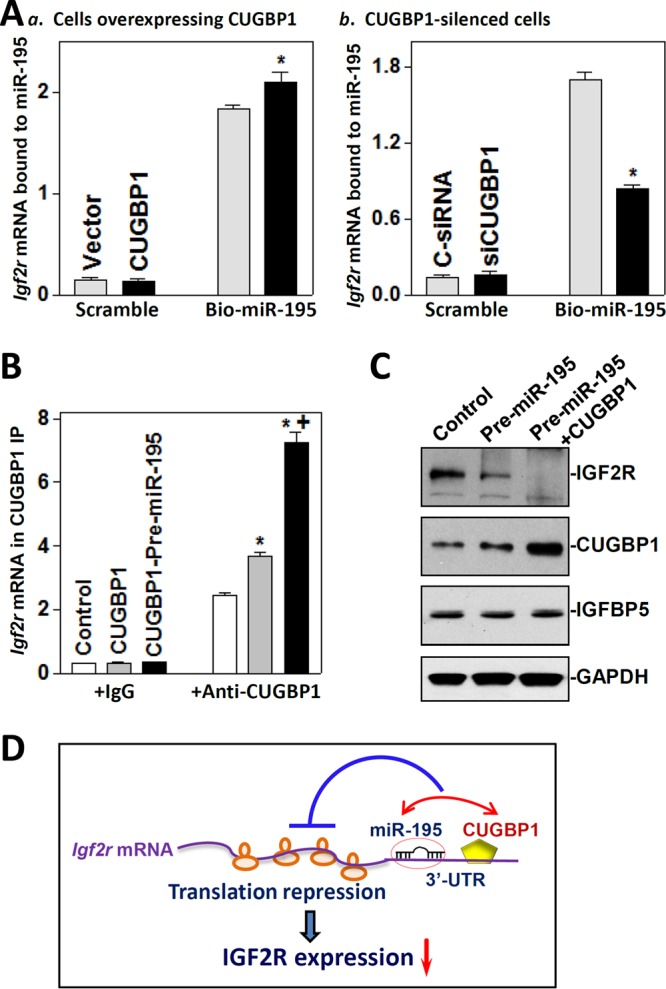
miR-195 and CUGBP1 inhibit IGF2R expression cooperatively. (A) Levels of Igf2r mRNA associated with miR-195 after increasing or decreasing cellular CUGBP1 abundance: (a) cells overexpressing CUGBP1; (b) CUGBP1-silenced cells. At 24 h after transfection with CUGBP1 expression vector or siCUGBP1, cells were transfected with biotinylated miR-195. The levels of Igf2r mRNA in biotin pulldown materials were measured 24 h after transfection with biotinylated miR-195. *, P < 0.05 (compared with cells transfected with control vector or C-siRNA). (B) Levels of the Igf2r mRNA associated with CUGBP1 in cells overexpressing CUGBP1 alone or both miR-195 and CUGBP1. Cells were transfected with CUGBP1 expression vector alone or both CUGBP1 and pre-miR-195, and the levels of Igf2r mRNA in CUGBP1 IP materials were examined 48 h after the transfection. Values represent means ± SEM of data from three separate experiments. * and +, P < 0.05 (compared with control and cells transfected with CUGBP1 alone, respectively). (C) Representative immunoblots of IGF2R, CUGBP1, and IGFBP5 in cells overexpressing both miR-195 and CUGBP1. At 48 h after the cotransfection with the CUGBP1 expression vector and pre-miR-195, the levels of different proteins were examined by Western immunoblotting analysis. (D) Proposed model to explain the cooperative repression of IGF2R translation by miR-195 and CUGBP1. Both miR-195 and CUGBP1 directly interacted with Igf2r mRNA, and the association of CUGBP1 with Igf2r mRNA enhanced miR-195 binding to Igf2r mRNA. This cooperative interaction between miR-195 and CUGBP1 synergistically inhibited IGF2R translation.
