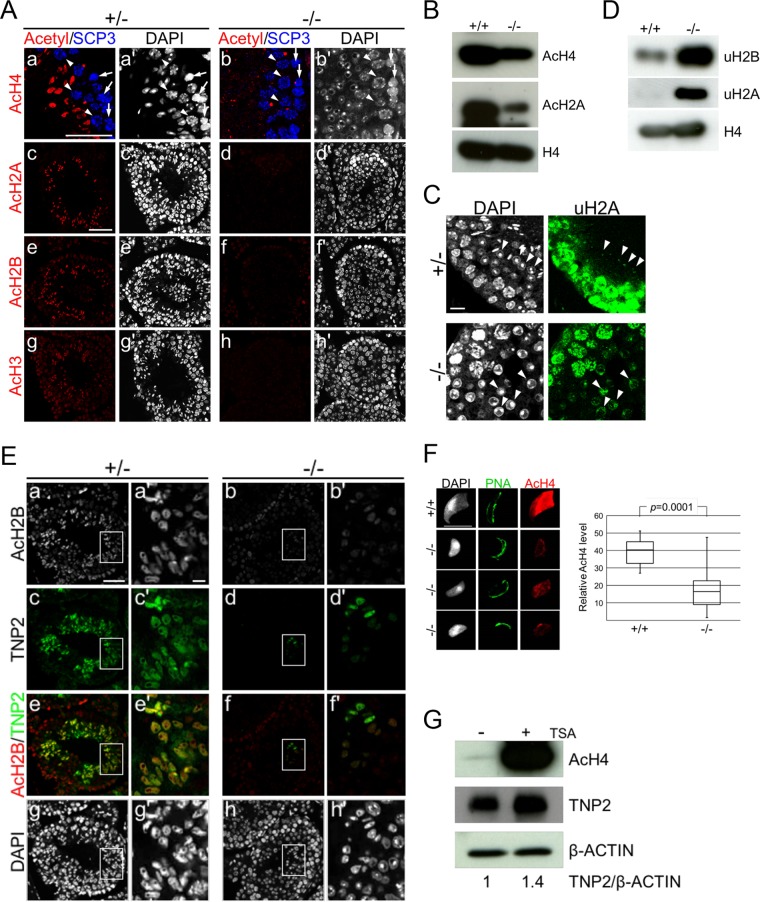
FIG 4.
Impaired histone hyperacetylation and TNP2 incorporation of Epc1-KO spermatids. (A) Defects in histone hyperacetylation in Epc1-KO spermatids. Paraffin sections were indirectly immunostained with anti-acetylated histone H4 (a and b), H2A (c and d), H2B (e and f), or H3 (g and h) antibody in Epc1-KO (−/−) spermatids and littermate heterozygotes (+/−). SCP3 antibody was used for detection of leptotene (arrows) and pachytene (arrowheads) spermatocytes and staging of seminiferous tubules (a, a′, b, and b′). In the presumed stage 9 seminiferous tubules of Epc1-KO mice; leptotene and pachytene spermatocytes were normally layered from basal membrane to seminiferous tubule lumen, but ESs containing hyperacetylated histone were hardly detectable. In addition, a layer of round spermatids was expanded. Scale bars, 50 μm. (B) Reduced histone acetylation levels in Epc1-KO germ cells. Acetylation levels of histone H4 (AcH4) and H2A (AcH2A) in adult germ cells were compared between Epc1-KO (−/−) and wild-type littermates (+/+) by IB analysis. (C) Excess accumulation of RSs demarcated by ubiquitinated histone H2A. Expression of ubiquitinated histone H2A (uH2A) in Epc1-KO seminiferous tubules was examined by IF analysis. Arrowheads indicate RSs. Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) Increased histone ubiquitination levels in Epc1-KO germ cells. Ubiquitination levels of histone H2A (uH2A) and H2B (uH2B) were examined by IB analysis in adult germ cells. (E) Partial restoration of elongating spermatids in Epc1-KO seminiferous tubules. Paraffin sections were immunostained for acetylated histone H2B and transition protein 2 (TNP2) in Epc1-KO mice (−/−) and littermate heterozygotes (+/−). A cluster of Epc1-KO spermatids exhibited a partial restoration of histone H2B acetylation (AcH2B) and a simultaneous incorporation of TNP2 along with an elongating morphology. Enlarged views for the boxed regions in panels a to h are shown in panels a′ to h′, respectively. Scale bars, 50 μm (a) and 5 μm (a′). (F) Partial restoration of histone acetylation levels in Epc1-KO spermatids with an elongating morphology. A spread preparation of spermatids (left) was used to examine morphology, PNA distribution, and histone H4 acetylation levels (AcH4). Representative elongating Epc1-KO spermatids that escaped from maturation arrest are shown. Scale bar, 10 μm. Relative quantification of histone H4 acetylation levels in elongating Epc1-KO (n = 32) and wild-type (n = 20) ESs was performed by using ImageJ, and the results are summarized by box plots (right). The boxes represent the interquartile deviation. (G) The impact of trichostatin A (TSA) treatment on histone H4 acetylation and TNP2 incorporation in Epc1-KO spermatids. Epc1-KO germ cells were cultured for 3 days with (+) or without (−) TSA and subjected to IB analyses for acetylated histone H4, TNP2, and β-actin. TNP2/β-actin ratios based on respective band intensities are shown at the bottom, in which the ratio in untreated Epc1-KO germ cells was set as 1.