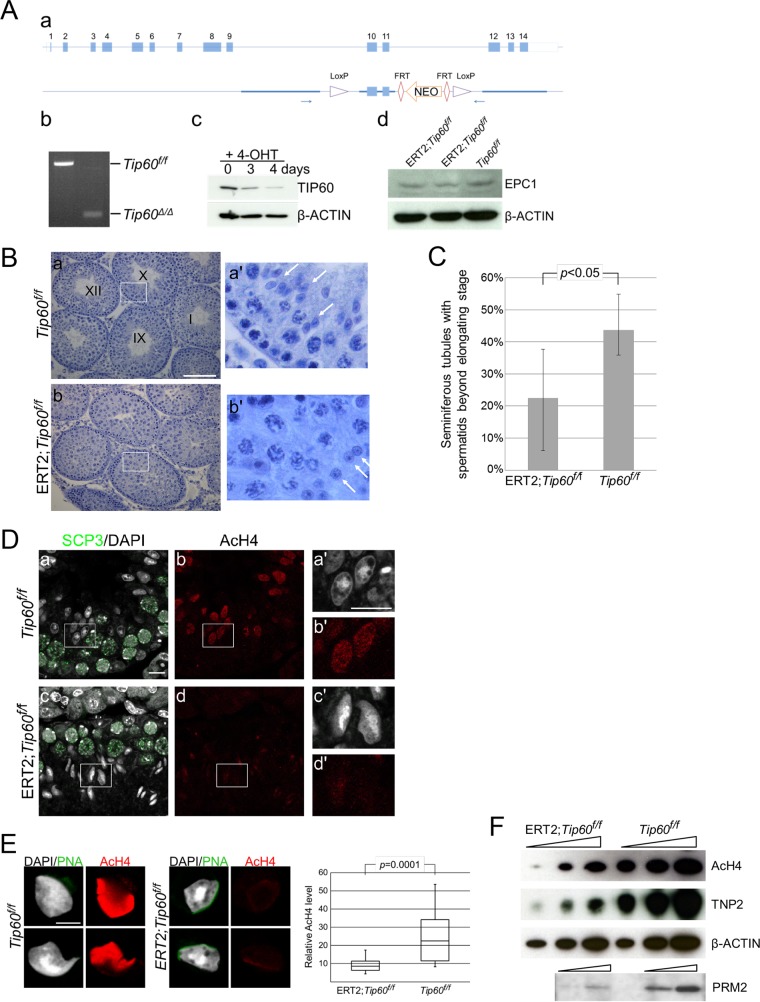
FIG 5.
Tip60 deletion affects histone acetylation and ES generation. (A) Generation of the Tip60-KO allele. (a) Schematic representation of the strategy to generate a conditional knockout allele of the Tip60 gene. FRT, Flp recognition target. (b) Cre-mediated deletion of exons 10 and 11 to generate the Tip60-KO (Tip60Δ/Δ) allele revealed by PCR analysis. (c) Reduction of TIP60 protein in Tip60-KO cells. We have established ERT2-Cre; Tip60flox/flox ES cells from blastocysts and induced Tip60 deletion upon 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) treatment. (d) EPC1 expression in Tip60-KO germ cells. Whole-cell lysates of germ cells from tamoxifen-injected ERT2-Cre; Tip60flox/flox mice were examined by IB analysis. (B) Morphological changes in moderately affected seminiferous tubules of Tip60-KO testes. (a) Seminiferous tubule stages of a control (Tip60flox/flox cells) are indicated numerically. (b) A section of Tip60-KO (ERT2; Tip60flox/flox) testes with developmental arrest of germ cells are shown. Note that lack of elongating spermatids in the presumed stage 9/10 seminiferous tubules of the Tip60-KO cells. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) Partial impairment of ES generation in ERT2; Tip60flox/flox mice treated by 4-hydroxytamoxifen. Frequency of seminiferous tubule sections containing ESs or more mature spermatids was calculated from five knockout (ERT2; Tip60flox/flox) and three control (Tip60flox/flox) samples. (D) Reduced acetylation level of histone H4 in Tip60-KO ESs. Stage 9/10 seminiferous tubules from a control and Tip60-KO mouse were immunostained with anti-SCP3 and anti-acetylated histone H4 (AcH4) antibodies. Acetylation levels in elongating spermatids from Tip60-KO mice were lower than those from controls in spite of their similar morphologies. Enlarged views for boxed regions in panels a to d are shown in panels a′ to d′, respectively. Scale bars, 50 μm (a) and 10 μm (a′). (E) Reduced acetylation level of histone H4 in Tip60-KO ESs. (Left) A spread preparation of spermatids was used to examine their morphology and histone H4 acetylation (AcH4) levels (left). Scale bar, 10 μm. Relative quantification for histone H4 acetylation levels in elongating Tip60-KO (n = 22) and control (n = 8) spermatids was performed by using ImageJ (right). (F) Reduction of histone H4 acetylation and TNP2 and PRM2 incorporation in Tip60-KO germ cells. Germ cells from tamoxifen-injected male mice were collected, and their lysates were subjected to IB analysis to examine histone acetylation, TNP2, and PRM2 levels. Tip60f/f, Tip60flox/flox.