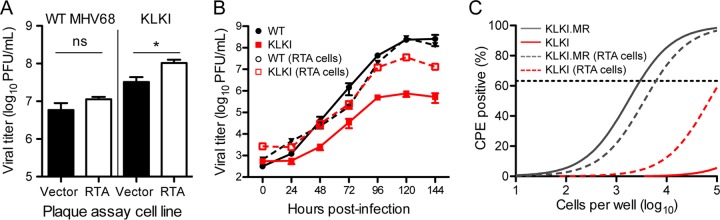
FIG 5.
Exogenous RTA bypasses KLKI MHV68 replication and reactivation defects. (A) WT MHV68 and KLKI MHV68 were titrated by plaque assay on 3T12 fibroblasts that stably expressed RTA or contained the empty vector. Data represent means of results from triplicate samples. Error bars represent standard errors of the means. *, P < 0.05 (determined using an unpaired, two-tailed Student's t test); ns, not significant. (B) NIH 3T12 fibroblasts were infected with WT, KLKI, KLKI.MR, or 73.STOP MHV68 at an MOI of 0.05 PFU/cell. Viral titers were determined at the indicated times postinfection by plaque assay on 3T12 fibroblasts that stably expressed RTA or contained the empty vector. (C) C57BL/6 mice were intranasally infected with 1,000 PFU of KLKI or KLKI.MR MHV68. Spleens were harvested on days 16 to 18 postinfection. Reactivation frequencies were determined by ex vivo plating of serially diluted cells on indicator monolayers of 3T12 fibroblasts that stably expressed RTA or contained an empty vector. Cytopathic effect (CPE) was scored 2 to 3 weeks postplating. Groups of 3 to 5 mice were pooled for each infection and analysis. Data represent means of results of two independent infections. Results of nonlinear regression analyses are shown.