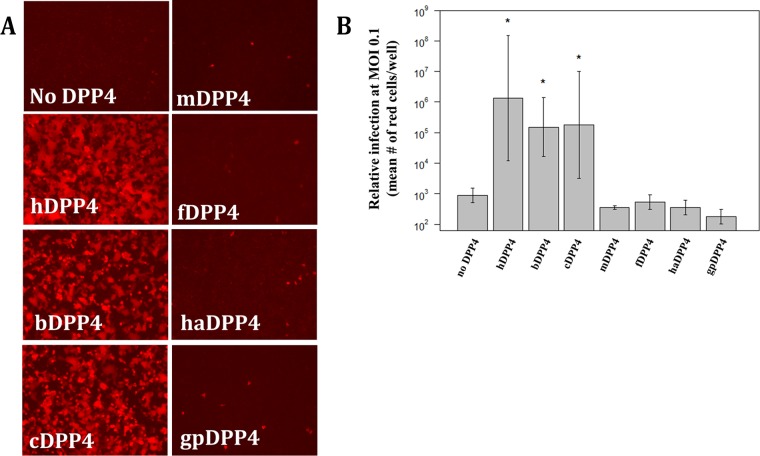
FIG 1.
Permissivity of DPP4 orthologs to MERS-CoV. (A) Seven DPP4 orthologs were tested for their ability to support infection by rMERS-CoV-RFP. DPP4 constructs were transfected into HEK 293T cells and infected at an MOI of 5 at ∼20 h posttransfection. Cells were imaged for fluorescence at ∼24 hpi. hDPP4, human DPP4; cDPP4, camel DPP4; bDPP4, bat DPP4; mDPP4, mouse DPP4; fDPP4, ferret DPP4; haDPP4, hamster DPP4; gpDPP4, guinea pig DPP4. (B) Mean fluorescent cell counts of MERS-CoV infection utilizing various DPP4 orthologs. Cells were infected at an MOI of 0.1 and the numbers of infected cells counted at ∼72 hpi. Each DPP4 ortholog was measured in triplicate. Only hDPP4, bDPP4, and cDPP4 had levels of infection significantly higher than those seen in the absence of DPP4 (*, P < 0.05 [Student's t test]). All DPP4 orthologs had significantly lower levels of infection than hDPP4 (P < 0.05 [Student's t test]). The levels of infection seen between bDPP4 and cDPP4 were not significantly different. Error bars indicate mean values ± 1 standard deviation.