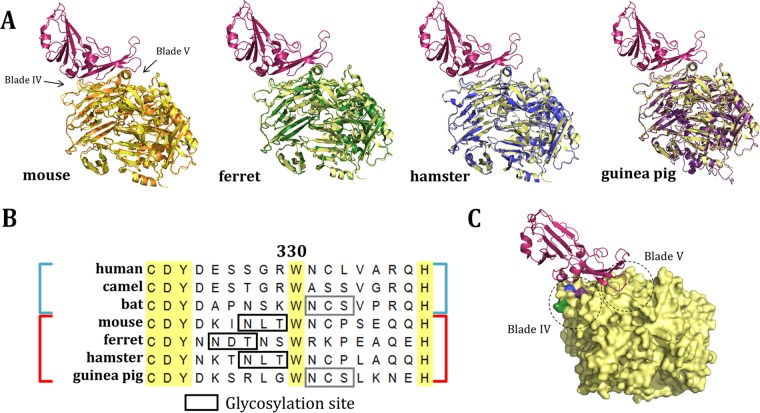
FIG 2.
Sequence and structural comparison of nonpermissive DPP4 orthologs. (A) Structural comparison of threaded molecules (30) of mDPP4 (orange), fDPP4 (green), haDPP4 (blue), and gpDPP4 (purple) overlaid on hDPP4 (yellow) complexed with the MERS-CoV RBD (red) (PDB code 4L72). (B) Sequence alignment of permissive (human, camel, bat; blue) and nonpermissive (mouse, ferret, hamster, guinea pig; red) DPP4 amino acid sequences. Residue 330 is numbered relative to mDPP4. Boxes represent glycosylation sites that are either unique to nonpermissive species (black) or shared with a permissive species (gray). (C) hDPP4 (yellow) complexed with the MERS-CoV RBD (red) (PDB code 4L72). Residues aligning to the ferret (green), hamster and mouse (blue), and guinea pig (purple) glycosylation sites are highlighted. Dashed-line circles indicate the regions of the DPP4 molecule that correspond to blades IV and V.