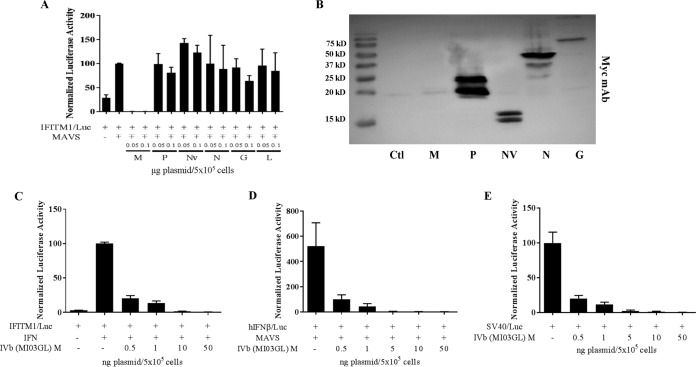
FIG 2.
VHSV-IVb M inhibits host promoter activation. (A) EPC cells were cotransfected with 0.4 μg of the IFITM1/luc construct, EPC-derived MAVS (0.3 μg), and plasmids encoding each of the VHSV genes (0.05 or 0.1 μg), followed by luciferase assay 48 h later. Luciferase values were normalized to those with IFITM1/luc plus MAVS. Plasmid concentrations in all samples were equalized with an empty vector. (B) EPC cells (1 × 106) were transfected with 2 μg of expression plasmids for the indicated VHSV proteins expressed in frame with a C-terminal Myc epitope tag. After 48 h, cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted for protein expression with a Myc MAb. Note that VHSV M is less highly expressed because of its ability to inhibit its own expression from the RNAP II-directed CMV promoter. (C) EPC cells were cotransfected with IFITM1/luc (0.4 μg) and various concentrations of a VHSV-IVb M expression plasmid (0.5 to 50 ng) for 24 h and then treated or not treated with EPC IFN for 24 h, followed by luciferase assay. Luciferase values were normalized to that for IFITM1/luc plus IFN. (D) EPC cells were cotransfected with human IFN (hIFN)/luc (0.4 μg), MAVS (0.3 μg), and various concentrations of a VHSV-IVb M expression plasmid (pCD-M; 0.5 to 50 ng) for 24 h, followed by luciferase assay. Luciferase values were normalized to that for IFN/luc plus MAVS. (E) EPC cells were cotransfected with a SV40/luc construct (0.4 μg) and various concentrations of pCD-M (0.5 to 50 ng) for 24 h, followed by luciferase assay. Luciferase values were normalized to that for SV40/luc alone. Ctl, control.