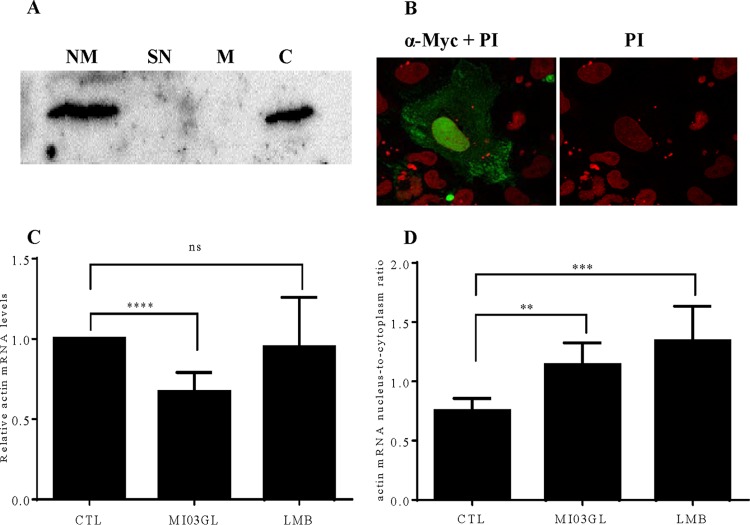
FIG 5.
VHSV IVb M localizes to the nucleus and cytoplasm and alters host mRNA dynamics. (A) Cells transiently transfected with pCD-M were fractionated into nuclear membrane (lane NM), soluble nuclear (lane SN), mitochondrial (lane M), and cytoplasmic (lane C) fractions using differential centrifugation. Lysates were run on a 15% SDS-PAGE gel and transferred to PVDF. IVb M was detected with a 1:1,000-diluted Myc antibody (Cell Signaling). (B) EPC cells were transfected with pCD-M for 24 h. Fixed/permeabilized cells were incubated with anti-Myc primary antibody and then goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody conjugated with FITC. Cells were counterstained with propidium iodide (PI) and viewed using a confocal microscope (magnification, ×100). (C) EPC cells were left uninfected or were infected with VHSV-IVb virus (MOI of 1) for 24 h or treated with leptomycin B (LMB) for 3 h. After infection/treatment, the EPC cell pellets were spiked with 1 × 105 HEK 293 cells before fractionation, which was followed by RNA isolation and RT-qPCR. (D) Total β-actin mRNA levels and ratios of nuclear fish actin mRNA to cytoplasmic fish actin mRNA were calculated. β-Actin values were normalized to human GAPDH values to control for differences in isolation efficiency under conditions in which nuclear/cytoplasmic levels of the human transcript were not altered by treatment. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.005; ****, P < 0.001.