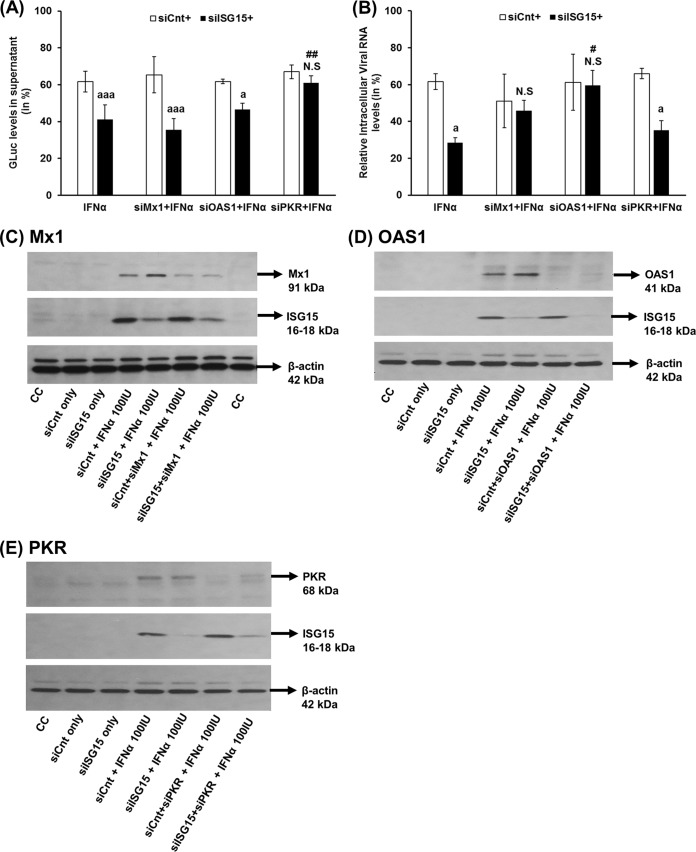
FIG 7.
ISG15 silencing mediates an enhanced antiviral effect of IFN-α against HEV via PKR and OAS1. Huh7-S10-3 liver cells were cotransfected with HEV RNA and control siRNA (siCnt)/ISG15-siRNA (siISG15), along with siRNA targeted against Mx1 (siMx1) or OAS1 (siOAS1) or PKR (siPKR). At 24 hpt, cells were either left untreated or treated with 100 IU/ml IFN-α. (A) GLuc activity levels in cell culture supernatant at 5 dpt. (B) Intracellular HEV P6 viral RNA levels. The relative changes in GLuc/viral RNA levels were calculated with respect to the corresponding IFN-α-untreated sample. (C to E) Representative Western blot analyses to show the siRNA knockdown efficiency. The Huh7-S10-3 liver cells were cotransfected with control siRNA (siCnt)/ISG15-siRNA (siISG15), along with siRNA targeted against Mx1 (siMx1) (C) or OAS1 (siOAS1) (D) or PKR (siPKR) (E). At 24 hpt, cells were either left untreated or treated with 100 IU/ml IFN-α. After 24 h post-IFN-α treatment, Mx1/PKR/OAS1 protein levels were estimated using Western blot analyses to determine the siRNA knockdown efficiency. The data represent means ± SEM of results from three independent experiments (A) and duplicate cultures (B). a, P ≤ 0.05; aaa, P ≤ 0.001 (compared to siCnt plus IFN-α); #, P ≤ 0.05; ##, P ≤ 0.01 (compared to siISG15 plus IFN-α). N.S, not significant.