Figure 3. Rab35 interacts with the zinc‐finger domain in NDP52.
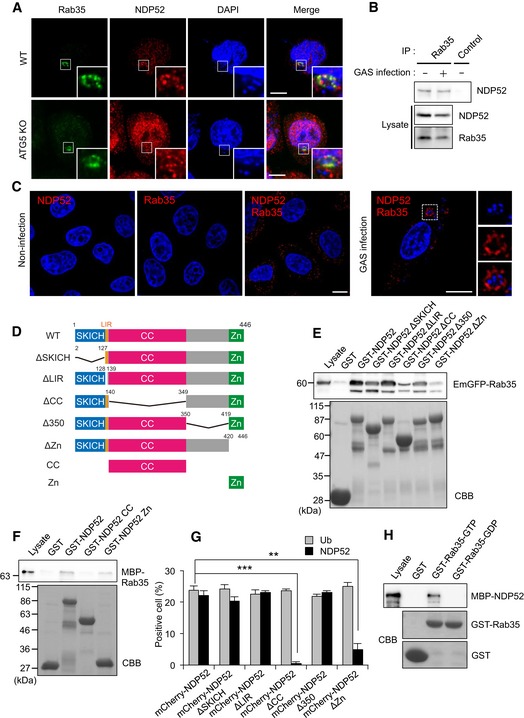
- Wild‐type and ATG5 knockout cells were infected with GAS for 4 h and immunostained with anti‐NDP52 and anti‐Rab35. Scale bars, 10 μm.
- Coimmunoprecipitation of endogenous Rab35 and NDP52 in uninfected HeLa cells and HeLa cells infected with GAS for 4 h.
- HeLa cells infected with or without GAS were stained with Rab35 and NDP52 primary antibodies to assess Rab35‐NDP52 binding by Duolink proximity ligation assay. Dots (red) indicate Rab35‐NDP52 complexes. Scale bars, 10 μm.
- Domain organization and deletion mutants of NDP52.
- HEK293T cells were transfected with EmGFP‐Rab35 and analyzed by pull‐down assay using immobilized GST or indicated GST‐NDP52 constructs. Rab35 was detected with anti‐GFP.
- Beads coated with GST or indicated GST‐NDP52 constructs were incubated with MBP‐Rab35 and immunoblotted with an antibody against MBP.
- Quantification of ubiquitin‐ and NDP52‐tagged bacteria, as measured by confocal microscopy. Data are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Data were tested by two‐tailed Student's t‐test: **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
- Beads coated with GST or GST‐Rab35 loaded with GDP or GTP were incubated with MBP‐NDP52 and immunoblotted with an anti‐MBP antibody.
Source data are available online for this figure.
